Longitudinal study of cognitive and mental functions among adult Hodgkin-lymphoma survivors, based on data from a primary treatment center in Hungary
- PMID: 40034597
- PMCID: PMC11872912
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1509424
Longitudinal study of cognitive and mental functions among adult Hodgkin-lymphoma survivors, based on data from a primary treatment center in Hungary
Abstract
Introduction: Due to risk and response-adapted treatment strategies, more than 80% of newly diagnosed adult classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients at any stage can be cured and become long-term survivors. A well-known side effect is cognitive dysfunction that appears in HL patients after chemotherapy (chemobrain). In the present longitudinal study, we measured cognitive function in our HL patients, in search of potential correlations between patient-related factors, the signs and symptoms of their diseases, and therapeutic factors.
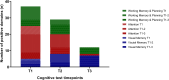
Methods: Patients underwent a computer-assisted assessment (CANTAB) of cognitive function (especially domains of visual memory, attention, working memory, and planning) and filled out psychological questionnaires (standardized, self-administered and validated for Hungarian language) before treatment (n=30, T1) and after the first-line treatment (n=25, T2), and 8.6 years after the end of chemotherapy (n=19, T3).
Results: The median age of 16 females and 14 males was 35 years (20-69), 35 years (21-63) after chemotherapy, and 43 years (29-70) at the end of the long-term follow-up, when the study was completed. 77% of all patients showed cognitive impairment before treatment. A close correlation was found between attention and unfavorable prognostic factors (III-IV. stage, age, bulky) baseline comorbidities (T2DM, psoriasis, HTN) and place of residence. Visual memory was affected by comorbidities and the place of residence. Working memory and planning was influenced by single marital status, and bulk disease. Post-treatment cognitive impairment was evaluated in 77% of the HL patients. In the working memory and planning domain, the Stockings of Cambridge (SOC) subtest significantly improved after treatment, while visual memory and attention remained unchanged. The cumulative dose of bleomycin associated with SOC.
Conclusion: The study highlights the fact that cognitive functions of HL patients were already impaired before treatment, especially attention, working memory, and planning. Long-term improvement in cognitive function was observed post-treatment. Employment status, place of residence and unfavorable prognosis have an impact on cognitive domains. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential to maintain patients' quality of life throughout and after treatment.
Keywords: Hodgkin-lymphoma; cancer-related cognitive impairment (CRCI); chemobrain; computerized neuropsychological test battery (CANTAB); health-related quality of life.
Copyright © 2025 Virga, Kósa, Illés, Miltényi, Ivánka, Berecz, Égerházi, Illés and Magyari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cancer Registry of National Institute of Oncology . Rákregiszter Statisztika(2023). Available online at: www.onkol.hu/en/rakregiszter-statisztika (Accessed November 12, 2023).
-
- Pinczés L. How the epidemiology of Hodgkin lymphoma changed in Debrecen, Hungary. Med Res Arch. (2016) 4:1–13. doi: 10.18103/mra.v4i6.658 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

