This is a preprint.
Genetic contributions to epigenetic-defined endotypes of allergic phenotypes in children
- PMID: 40034775
- PMCID: PMC11875257
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.10.03.24314618
Genetic contributions to epigenetic-defined endotypes of allergic phenotypes in children
Update in
-
Genetic contributions to epigenetic-defined endotypes of allergic phenotypes in children.Am J Hum Genet. 2025 Jul 3;112(7):1610-1624. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2025.05.006. Am J Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 40614707 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Asthma is the most common chronic respiratory disease in children, but little is known about genetic contributions to its underlying endotypes. To address this gap, we studied the methylome, transcriptome, and genome from children with extensive phenotyping from birth.
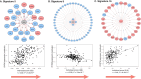
Methods: We performed DNA methylation (DNAm) studies using the Asthma&Allergy array and RNA-sequencing in nasal mucosal cells from 284 children (age 11 years) in the Urban Environment and Childhood Asthma (URECA) birth cohort with genotypes from whole-genome sequencing. Using empirical Bayes matrix factorization on all CpGs on the array, we derived 16 DNAm signatures and tested for associations between phenotypes and gene expression. We then replicated results in two additional cohorts and estimated the heritability of phenotype-associated signatures using single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with an allergic disease, and with CpGs and genes associated with the signatures.
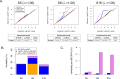
Findings: Three DNAm signatures were associated with at least one phenotype: allergic asthma, allergic rhinitis, allergic sensitization (atopy), total IgE, exhaled nitric oxide, or blood eosinophils. The genes correlated with each of the three signatures were enriched in networks reflecting inhibited immune response to microbes, impaired epithelial barrier integrity, and activated T2 immune pathways. We replicated the signature-phenotype associations in two additional birth cohorts. The estimated joint SNP heritabilities of the signatures were 0.17 (p=0.0027), 0.30 (p=9.3×10-7), and 0.16 (p=9.0×10-7), respectively.
Interpretation: We identified three significantly heritable DNAm signatures defining asthma and allergy endotypes across diverse populations. Our study demonstrated that epigenetic patterning in airway mucosal cells reflects perturbations in underlying biological processes related to the development of asthma and allergic diseases in childhood.
Funding: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Dr. Bacharier is a member of the GINA Science Committee; reports grants from NIH/NIAID/NHLBI, personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech/Novartis, Merck, Teva, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Avillion, WebMD/Medscape, Sanofi/Regeneron, Vectura, Circassia, OM Pharma and Kinaset, for DSMB from AstraZeneca, DBV Technologies, and Vertex; and royalties from Elesvier outside the submitted work. Dr. Wood receives research support from the NIH, Aimmune, ALK, DBV, Genentech, Novartis, Siolta, and FARE, and consulting fees from Genentech. Dr. Zoratti reported grants from NIH during the conduct of the study. Dr. Hartert reported grants from NIH and the World Health Organization during the conduct of the study and personal fees from the American Thoracic Society, Parker B. Francis Council of Scientific Advisors, Pfizer and Sanofi-Pasteur outside the submitted work. Dr. Stephens reported grants from the NIH during the conduct of the study Dr. Jackson has received funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Regeneron; personal fees for Data and Safety Monitoring Board from Pfizer and AstraZeneca; and personal fees for consulting from AstraZeneca, Avillion, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, and Regeneron. Dr. Gern reported grants from NIH during the conduct of the study, personal fees from Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Meissa Vaccines Inc., and stock options for Meissa Vaccines Inc. outside the submitted work. Dr. McKennan reported grants from the NIH during the conduct of the study and personal fees from SignatureDx outside the submitted work. Dr. Ober reported grants from the NIH during the conduct of the study. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pinart M, Benet M, Annesi-Maesano I, et al. Comorbidity of eczema, rhinitis, and asthma in IgE-sensitised and non-IgE-sensitised children in MeDALL: a population-based cohort study. Lancet Respir Med 2014; 2(2): 131–40. - PubMed
-
- Holgate ST. Epithelium dysfunction in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120(6): 1233–44; quiz 45–6. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- P01 ES009600/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025496/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI059415/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI050681/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES008977/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL064305/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES013163/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272200900052C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD061879/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HG002585/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI061774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035786/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI110450/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES022321/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES019890/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000533/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025482/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI069271/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025771/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023282/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI070606/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI060040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI095230/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000071/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI114271/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002585/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG080590/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI080066/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023282/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011170/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI089473/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050681/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL070831/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI060040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI095227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201000052I/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051598/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES009089/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD082147/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
