Ultrasound Beyond Joints: A Review of Extra-Articular Applications in Rheumatology
- PMID: 40035992
- PMCID: PMC11880079
- DOI: 10.1007/s11926-025-01186-9
Ultrasound Beyond Joints: A Review of Extra-Articular Applications in Rheumatology
Abstract
Purpose of review: This review highlights key ultrasound applications for evaluating extra-articular involvement in rheumatic diseases, including the lungs, vessels, salivary glands, muscles, nerves, skin, and nails. It explores recent advances, emerging areas of assessment, and future research directions. Additionally, the review examines current limitations in the routine use of ultrasound for these purposes and considers the potential of new technologies, such as shear-wave elastography, contrast-enhanced ultrasound, and artificial intelligence, to enhance the early detection and monitoring of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatic diseases.
Recent findings: Extra-articular manifestations in patients with rheumatic diseases are crucial for diagnosis, management (including treatment strategies), and prognosis, making accurate assessment essential. Growing evidence supports the role of ultrasound in assessing these manifestations for diagnosis, monitoring, and gaining insights into disease pathogenesis. Recent studies emphasize the significant utility of ultrasound in evaluating extra-articular involvement across various organ systems, including the lungs, vessels, salivary glands, muscles, nerves, skin, and nails. Technological advances, such as shear-wave elastography, contrast-enhanced ultrasound, and artificial intelligence, are expanding the scope and precision of ultrasound applications. Despite its potential, challenges such as operator dependency, lack of standardized protocols, and the need for specialized training hinder its widespread adoption. Ultrasound is a non-invasive, cost-effective, and radiation-free imaging modality with high diagnostic accuracy, making it a valuable tool for assessing extra-articular manifestations in rheumatic diseases. Emerging technologies may further enhance its clinical utility. However, efforts to standardize techniques and improve accessibility are necessary to optimize its integration into routine practice.
Keywords: Extra-articular; Interstitial lung disease; Large vessel vasculitis; Muscle; Nail; Nerve; Salivary gland; Skin; Ultrasound.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

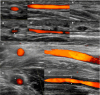
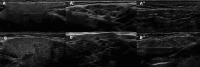

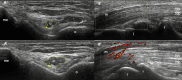
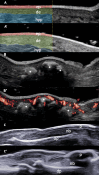
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

