The role of AGEs in muscle ageing and sarcopenia
- PMID: 40036085
- PMCID: PMC11878473
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.143.BJR-2024-0252.R1
The role of AGEs in muscle ageing and sarcopenia
Abstract
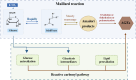
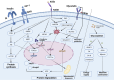
Sarcopenia is an ageing-related disease featured by the loss of skeletal muscle quality and function. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are a complex set of modified proteins or lipids by non-enzymatic glycosylation and oxidation. The formation of AGEs is irreversible, and they accumulate in tissues with increasing age. Currently, AGEs, as a biomarker of ageing, are viewed as a risk factor for sarcopenia. AGE accumulation could cause harmful effects in the human body such as elevated inflammation levels, enhanced oxidative stress, and targeted glycosylation of proteins inside and outside the cells. Several studies have illustrated the pathogenic role of AGEs in sarcopenia, which includes promoting skeletal muscle atrophy, impairing muscle regeneration, disrupting the normal structure of skeletal muscle extracellular matrix, and contributing to neuromuscular junction lesion and vascular disorders. This article reviews studies focused on the pathogenic role of AGEs in sarcopenia and the potential mechanisms of the detrimental effects, aiming to provide new insights into the pathogenesis of sarcopenia and develop novel methods for the prevention and therapy of sarcopenia.
© 2025 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Y. Li reports funding from National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2023YFC3603400), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82472522, 92268115), and National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders (Xiangya Hospital, No. 2021KF02), related to this study. Y. Wu reports funding from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82472495, 82071970, 81971775), related to this study. Z. Deng reports funding from Basic Public Welfare Research projects of Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau (Y20240087) and Start-up Funding for Talented Scientific Research of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (2023QD026), related to this study.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

