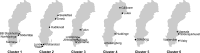Can the use of a next generation partograph based on WHO's latest intrapartum care recommendations improve neonatal outcomes? (PICRINO) Study protocol for a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial
- PMID: 40036215
- PMCID: PMC11878932
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316336
Can the use of a next generation partograph based on WHO's latest intrapartum care recommendations improve neonatal outcomes? (PICRINO) Study protocol for a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial
Abstract
Background: Monitoring labor and childbirth, early recognition, and treatment of complications are critical for preventing adverse birth outcomes. However excessive use of interventions during labor has not been demonstrated to enhance subsequent birth outcomes and may, in fact, pose a risk of harm. The World Health Organization has recently synthesized research from the last decade concerning labor progress and patient-centered care into a new recommendation: the Labour Care Guide (LCG). No trial has, however, compared the LCG with standard care regarding adverse neonatal outcomes or the degree of safety associated with implementing this recommendation within a high-resource setting, and its potential to enhance birth outcomes remains undetermined.
Aim and hypothesis: This trial aims to evaluate the impacts of using two different guidelines for monitoring labor with respect to neonatal and maternal outcomes, the LCG and the currently used standard care guideline. The hypothesis is that use of the LCG will reduce the number of adverse neonatal outcomes and decrease the rate of intrapartum cesarean sections, as compared with standard care.
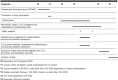
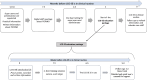
Materials and methods: A national, multicenter, stepped-wedge cluster randomized controlled trial that includes 24 Swedish maternity wards randomized to six clusters. The trial is planned to run during a 22 month period in 2023-2025 and the intervention LCG will be implemented in the six clusters, with three months intervals. The recruited wards will together have approximatively 100,000 births during the study period. Outcome data will be extracted from the Swedish national pregnancy, neonatal, and patient registers. Two safety analyses will be performed at one-third and two-thirds of the way through the trial.
Discussion: The LCG offers a promising new approach, but its effectiveness and safety in high resource settings remain unexplored and must be studied further before LCG can be fully implemented in settings with similar health care.
Trial registration: The trial has been registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov: NCT05560802.
Copyright: © 2025 Isgren et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Continuous cardiotocography (CTG) as a form of electronic fetal monitoring (EFM) for fetal assessment during labour.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 3;2(2):CD006066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006066.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28157275 Free PMC article.
-
Fundal pressure during the second stage of labour.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 7;3(3):CD006067. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006067.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28267223 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and support during early labour for improving birth outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 20;4(4):CD011516. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011516.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28426160 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture or acupressure for induction of labour.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 17;10(10):CD002962. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002962.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29036756 Free PMC article.
-
Epidural versus non-epidural or no analgesia for pain management in labour.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 21;5(5):CD000331. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000331.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29781504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. WHO recommendations. Intrapartum care for a positive childbirth experience. WHO guidelines approved by the guidelines review committee. Available from: https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/intrapartum-care-gui... - PubMed