A detailed analysis of second and third-generation sequencing approaches for accurate length determination of short tandem repeats and homopolymers
- PMID: 40036507
- PMCID: PMC11878640
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf131
A detailed analysis of second and third-generation sequencing approaches for accurate length determination of short tandem repeats and homopolymers
Abstract
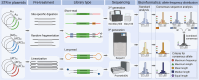
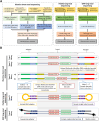
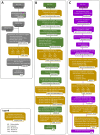
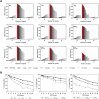
Microsatellites are short tandem repeats (STRs) of a motif of 1-6 nucleotides that are ubiquitous in almost all genomes and widely used in many biomedical applications. However, despite the development of next-generation sequencing (NGS) over the past two decades with new technologies coming to the market, accurately sequencing and genotyping STRs, particularly homopolymers, remain very challenging today due to several technical limitations. This leads in many cases to erroneous allele calls and difficulty in correctly identifying the genuine allele distribution in a sample. Here, we assessed several second and third-generation sequencing approaches in their capability to correctly determine the length of microsatellites using plasmids containing A/T homopolymers, AC/TG or AT/TA dinucleotide STRs of variable length. Standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-free and PCR-containing, single Unique Molecular Indentifier (UMI) and dual UMI 'duplex sequencing' protocols were evaluated using Illumina short-read sequencing, and two PCR-free protocols using PacBio and Oxford Nanopore Technologies long-read sequencing. Several bioinformatics algorithms were developed to correctly identify microsatellite alleles from sequencing data, including four and two modes for generating standard and combined consensus alleles, respectively. We provided a detailed analysis and comparison of these approaches and made several recommendations for the accurate determination of microsatellite allele length.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

