Injectable hydrogel with miR-222-engineered extracellular vesicles ameliorates myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury via mechanotransduction
- PMID: 40037358
- PMCID: PMC11970392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.101987
Injectable hydrogel with miR-222-engineered extracellular vesicles ameliorates myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury via mechanotransduction
Abstract
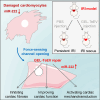
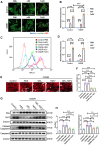
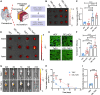
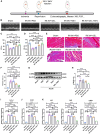
Cardiac ischemic reperfusion injury (IRI) significantly exacerbates cardiac dysfunction and heart failure, causing high mortality. Despite the severity of IRI, effective therapeutic strategies remain elusive. Acellular cardiac patches have shown considerable efficacy in delivering therapeutics directly to cardiac tissues. Herein, we develop injectable GelMA (GEL) hydrogels with controlled mechanical properties. Targeting miR-222-engineered extracellular vesicles (TeEVs), tailored with cardiac-ischemia-targeting peptides (CTPs), are developed as ischemic TeEV therapeutics. These TeEVs are encapsulated within mechanical hydrogels to create injectable TeEV-loaded cardiac patches, enabling minimal invasiveness to attenuate IRI. The injectable patches facilitate the precise targeting of TeEVs for the efficient rescue of damaged cells. Persistent delivery of TeEVs into the infarcted region alleviates acute IRI and mitigated remodeling post IRI. This is linked to focal adhesion activation, cytoskeleton force enhancement, and nuclear force-sensing preservation. These findings may pave the way for force-sensing approaches to cardiac therapy using bioengineered therapeutic patches.
Keywords: IRI remodeling; force-sensing mechanotransduction; injectable hydrogel patch; miR-222-engineered EV; targeting cardiac peptide.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


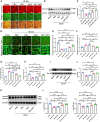
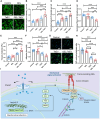
References
-
- Goldfarb M.J., Saylor M.A., Bozkurt B., Code J., Di Palo K.E., Durante A., Flanary K., Masterson Creber R., Ogunniyi M.O., Rodriguez F., et al. Patient-Centered Adult Cardiovascular Care: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149:e1176–e1188. - PubMed
-
- Richalet J.P., Hermand E., Lhuissier F.J. Cardiovascular Physiology and Pathophysiology at High Altitude. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2024;21:75–88. - PubMed
-
- Wang L., Qiu S., Li X., Zhang Y., Huo M., Shi J. Myocardial-Targeting Tannic Cerium Nanocatalyst Attenuates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023;62 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

