PARP inhibitor radiosensitization enhances anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy through stabilizing chemokine mRNA in small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40038278
- PMCID: PMC11880360
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57257-z
PARP inhibitor radiosensitization enhances anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy through stabilizing chemokine mRNA in small cell lung cancer
Abstract
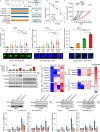
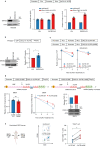
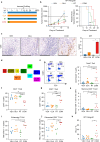
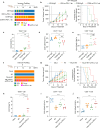
Immunotherapy (IO) is an effective treatment for various cancers; however, the benefits are modest for small cell lung cancer (SCLC). The poor response of SCLC to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 IO is due in part to the lack of cytotoxic T cells because of limited chemokine expression from SCLC tumors. Immunogenic radiosensitizers that enhance chemokine expression may be a promising strategy forward. Here, we show that the PARP inhibitors (PARPi), including olaparib, talazoparib and veliparib, in combination with radiotherapy (RT) enhance the immune activation and anti-tumor efficacy in SCLC cell lines, patient-derived xenograft (PDX) and syngeneic mouse models. The effect is further enhanced by continued delivery of adjuvant PARPi. The combination treatment (PARPi with RT) activates the cGAS-STING pathway and increases the mRNA levels of the T cell chemo-attractants CCL5 and CXCL10. In addition to upregulation of transcription, the combination treatment increases chemokine CXCL10 protein levels via stabilization of CXCL10 mRNA in an EIF4E2-dependent manner. The incorporation of anti-PD-L1 IO into the PARPi with RT combination therapy further improves the anti-tumor efficacy by increasing T cell infiltration and function. This study thus provides a proof of principle for the combination of PARP inhibitors, RT and anti-PD-L1 IO as a treatment strategy for SCLC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: B.H.L. reports grants from Pfizer; and grants, personal fees, and non-financial support from AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Galvis, M. M. et al. Immunotherapy improves efficacy and safety of patients with HPV positive and negative head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol.150, 102966 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Gandhi, L. et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.378, 2078–2092 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

