Inhibition of the STAT3/Fanconi anemia axis is synthetic lethal with PARP inhibition in breast cancer
- PMID: 40038300
- PMCID: PMC11880418
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57476-4
Inhibition of the STAT3/Fanconi anemia axis is synthetic lethal with PARP inhibition in breast cancer
Abstract
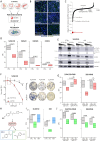
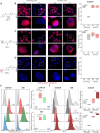
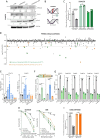
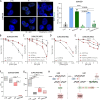
The targeting of cancer stem cells (CSCs) has proven to be an effective approach for limiting tumor progression, thus necessitating the identification of new drugs with anti-CSC activity. Through a high-throughput drug repositioning screen, we identify the antibiotic Nifuroxazide (NIF) as a potent anti-CSC compound. Utilizing a click chemistry strategy, we demonstrate that NIF is a prodrug that is specifically bioactivated in breast CSCs. Mechanistically, NIF-induced CSC death is a result of a synergistic action that combines the generation of DNA interstrand crosslinks with the inhibition of the Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway activity. NIF treatment mimics FA-deficiency through the inhibition of STAT3, which we identify as a non-canonical transcription factor of FA-related genes. NIF induces a chemical HRDness (Homologous Recombination Deficiency) in CSCs that (re)sensitizes breast cancers with innate or acquired resistance to PARP inhibitor (PARPi) in patient-derived xenograft models. Our results suggest that NIF may be useful in combination with PARPi for the treatment of breast tumors, regardless of their HRD status.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interest
Figures

References
-
- O’Brien, C. A., Pollett, A., Gallinger, S. & Dick, J. E. A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature445, 106–110 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Singh, S. K. et al. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature432, 396–401 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Eppert, K. et al. Stem cell gene expression programs influence clinical outcome in human leukemia. Nat. Med.17, 1086–1093 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

