Machine learning aided UV absorbance spectroscopy for microbial contamination in cell therapy products
- PMID: 40038316
- PMCID: PMC11880552
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83114-y
Machine learning aided UV absorbance spectroscopy for microbial contamination in cell therapy products
Abstract
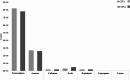
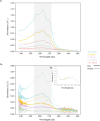
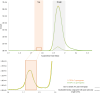
We demonstrate the feasibility of machine-learning aided UV absorbance spectroscopy for in-process microbial contamination detection during cell therapy product (CTP) manufacturing. This method leverages a one-class support vector machine to analyse the absorbance spectra of cell cultures and predict if a sample is sterile or contaminated. This label-free technique provides a rapid output (< 30 minutes) with minimal sample preparation and volume (< 1 mL). Spiking of 7 microbial organisms into mesenchymal stromal cells supernatant aliquots from 6 commercial donors showed that contamination events could be detected at low inoculums of 10 CFUs with mean true positive and negative rates of 92.7% and 77.7% respectively. The true negative rate further improved to 92% after excluding samples from a single donor with anomalously high nicotinic acid. In cells spiked with 10 CFUs of E. coli, contamination was detected at the 21-hour timepoint, demonstrating comparable sensitivity to compendial USP < 71 > test (~ 24 hours). We hypothesize that spectral differences between nicotinic acid and nicotinamide in the UV region are the underlying mechanisms for contamination detection. This approach can be deployed as a preliminary test during different CTP manufacturing stages, for real-time, continuous culture monitoring enabling early detection of microbial contamination, assuring safety of CTP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The ratio of nicotinic acid to nicotinamide as a microbial biomarker for assessing cell therapy product sterility.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2022 Apr 13;25:410-424. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.04.006. eCollection 2022 Jun 9. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2022. PMID: 35573051 Free PMC article.
-
Biological contaminants analysis in microalgae culture by UV-vis spectroscopy and machine learning.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025 Apr 5;330:125690. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2024.125690. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025. PMID: 39778393
-
Machine learning-based detection of adventitious microbes in T-cell therapy cultures using long-read sequencing.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 30;11(5):e0135023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01350-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37646508 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial contamination of cellular products for hematolymphoid transplantation therapy: assessment of the problem and strategies to minimize the clinical impact.Cytotherapy. 2003;5(5):377-90. doi: 10.1080/14653240310003044. Cytotherapy. 2003. PMID: 14578100 Review.
-
Validation Study of Rapid Assays of Bioburden, Endotoxins and Other Contamination.Biocontrol Sci. 2016;21(2):63-72. doi: 10.4265/bio.21.63. Biocontrol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27350424 Review.
References
-
- Ali, S. Microbial and viral contamination of animal and stem cell cultures: Common contaminants, detection and elimination. JSRT 2, (2017).
-
- USP. 71 STERILITY TESTS.pdf.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

