Dynamical analysis and numerical assessment of the 2019-nCoV virus transmission with optimal control
- PMID: 40038386
- PMCID: PMC11880544
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-90915-2
Dynamical analysis and numerical assessment of the 2019-nCoV virus transmission with optimal control
Abstract
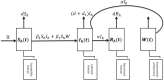
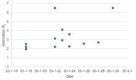
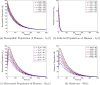
In this article, we discuss the qualitative analysis and develop an optimal control mechanism to study the dynamics of the novel coronavirus disease (2019-nCoV) transmission using an epidemiological model. With the help of a suitable mathematical model, health officials often can take positive measures to control the infection. To develop the model, we assume two disease transmission sources (humans and reservoirs) keeping in view the characteristics of novel coronavirus transmission. We formulate the model to study the temporal dynamics and determine an optimal control mechanism to minimize the infected population and control the spreading of the novel coronavirus disease propagation. In addition, to understand the significance of each model parameter, we compute the threshold quantity and perform the sensitivity analysis of the basic reproductive number. Based on the temporal dynamics of the model and sensitivity analysis of the threshold parameter, we develop a control mechanism to identify the best control policy for eradicating the disease. We then conduct numerical experiments using large-scale numerical simulations to validate the theoretical findings.
Keywords: Epidemiological model; Numerical simulation; Optimal control theory; Stability analysis; Threshold parameter.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Azhar, E. I. et al. Evidence for camel-to-human transmission of mers coronavirus. N. Engl. J. Med.370(26), 2499–2505 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Chen, Z. et al. From sars-cov to wuhan 2019-ncov outbreak: Similarity of early epidemic and prediction of future trends. CELL-HOST-MICROBE-D-20-00063, (2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

