The protective PLCγ2-P522R variant mitigates Alzheimer's disease-associated pathologies by enhancing beneficial microglial functions
- PMID: 40038760
- PMCID: PMC11881468
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03387-6
The protective PLCγ2-P522R variant mitigates Alzheimer's disease-associated pathologies by enhancing beneficial microglial functions
Abstract
Background: Phospholipase C gamma 2, proline 522 to arginine (PLCγ2-P522R) is a protective variant that reduces the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Recently, it was shown to mitigate β-amyloid pathology in a 5XFAD mouse model of AD. Here, we investigated the protective functions of the PLCγ2-P522R variant in a less aggressive APP/PS1 mouse model of AD and assessed the underlying cellular mechanisms using mouse and human microglial models.
Methods: The effects of the protective PLCγ2-P522R variant on microglial activation, AD-associated β-amyloid and neuronal pathologies, and behavioral changes were investigated in PLCγ2-P522R knock-in variant mice crossbred with APP/PS1 mice. Transcriptomic, proteomic, and functional studies were carried out using microglia isolated from mice carrying the PLCγ2-P522R variant. Finally, microglia-like cell models generated from human blood and skin biopsy samples of PLCγ2-P522R variant carriers were employed.
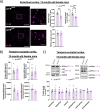
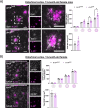
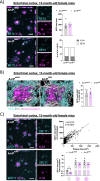
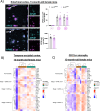
Results: The PLCγ2-P522R variant decreased β-amyloid plaque count and coverage in female APP/PS1 mice. Moreover, the PLCγ2-P522R variant promoted anxiety in these mice. The area of the microglia around β-amyloid plaques was also increased in mice carrying the PLCγ2-P522R variant, while β-amyloid plaque-associated neuronal dystrophy and the levels of certain cytokines, including IL-6 and IL-1β, were reduced. These alterations were revealed through [18F]FEPPA PET imaging and behavioral studies, as well as various cytokine immunoassays, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses, and immunohistochemical analyses using mouse brain tissues. In cultured mouse primary microglia, the PLCγ2-P522R variant reduced the size of lipid droplets. Furthermore, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses revealed that the PLCγ2-P522R variant regulated key targets and pathways involved in lipid metabolism, mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation, and inflammatory/interferon signaling in acutely isolated adult mouse microglia and human monocyte-derived microglia-like cells. Finally, the PLCγ2-P522R variant also increased mitochondrial respiration in human iPSC-derived microglia.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the PLCγ2-P522R variant exerts protective effects against β-amyloid and neuronal pathologies by increasing microglial responsiveness to β-amyloid plaques in APP/PS1 mice. The changes observed in lipid/fatty acid and mitochondrial metabolism revealed by the omics and metabolic assessments of mouse and human microglial models suggest that the protective effects of the PLCγ2-P522R variant are potentially associated with increased metabolic capacity of microglia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Lipid droplets; Microglia; PLCγ2-P522R variant; Phospholipase C gamma 2; β-amyloid pathology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The animals were raised and handled at the Laboratory Animal Center of the University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland. All mouse studies were carried out in accordance with the guidelines of the European Community Council Directives 86/609/EEC and approved by the Regional State Administrative Agency and Project Authorization Board (ESAVI/7315/2024, EKS-004–2019). All study protocols concerning human samples were approved by the Medical Research Ethics Committee of Wellbeing Services County of North Savo (formerly the Medical Research Ethics Committee of North Savo Hospital District, 833/2023, 123/2016). Participant recontacting was approved by the Scientific Steering Committee of Auria Biobank (BB_2020-0062). Consent for publication: All the authors have approved the final version of the manuscript and provided their consent for publication. Competing interests: CH collaborates with Denali Therapeutics and is a member of the advisory boards of AviadoBio and Cure Ventures.
Figures





References
-
- Bill CA, Vines CM, Phospholipase C. Calcium Signaling. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020.
-
- Keren-Shaul H, Spinrad A, Weiner A, Matcovitch-Natan O, Dvir-Szternfeld R, Ulland TK, et al. A unique microglia type associated with restricting development of alzheimer’s disease. Cell. 2017;169(7):1276-1290.e17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 330178/Research Council of Finland
- 355604/Research Council of Finland
- 337530/Research Council of Finland
- 338182/Research Council of Finland
- ADSF-24-1284326-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- 01ED2007A/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung grant
- 115975/Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking which receives support from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- 334802/JPco-fuND-2 'Multinational research projects on Personalized Medicine for Neurodegenerative Diseases' (PMG-AD)
- 390857198/the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) under Germany's Excellence Strategy within the framework of the Munich Cluster for Systems Neurology (EXC 2145 SyNergy)
- FKZ161L0214C/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung grant, ClinspectM
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

