Understanding social media discourse on antidepressants: unsupervised and sentiment analysis using X
- PMID: 40040572
- PMCID: PMC12041734
- DOI: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2025.10
Understanding social media discourse on antidepressants: unsupervised and sentiment analysis using X
Abstract
Background: Antidepressants are essential in managing depression, including treatment-resistant cases. Public perceptions of these medications, shaped by social media platforms like X (formerly Twitter), can influence treatment adherence and outcomes. This study explores public attitudes toward antidepressants through sentiment and topic modeling analysis of tweets in English and Spanish from 2007 to 2022.
Methods: Tweets mentioning antidepressants approved for depression were collected. The analysis focused on selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and glutamatergic drugs. Sentiment analysis and topic modeling were conducted to identify trends, concerns, and emotions in discussions across both languages.
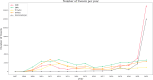
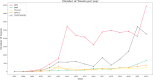
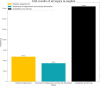
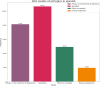
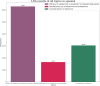
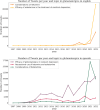
Results: A total of 1,448,674 tweets were analyzed (1,013,128 in English and 435,546 in Spanish). SSRIs were the most mentioned antidepressants (27.9% in English, 58.91% in Spanish). Pricing and availability were key concerns in English tweets, while Spanish tweets highlighted availability, efficacy, and sexual side effects. Glutamatergic drugs, especially esketamine, gained attention (15.61% in English, 25.23% in Spanish), evoking emotions such as fear, sadness, and anger. Temporal analysis showed significant increases in discussions, with peaks in 2012 and 2021 for SSRIs in Spanish, and exponential growth from 2018 to 2021 for glutamatergic drugs. Emotional tones varied across languages, reflecting cultural differences.
Conclusions: Social media platforms like X provide valuable insights into public perceptions of antidepressants, highlighting cultural variations in attitudes. Understanding these perceptions can help clinicians address concerns and misconceptions, fostering informed treatment decisions. The limitations of social media data call for careful interpretation, emphasizing the need for continued research to improve pharmacovigilance and public health strategies.
Keywords: antidepressants; esketamine; selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; sentiment analysis; twitter (X).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Salazar-de-Pablo has received honoraria from Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Angelini, and Menarini. Dr. Gonzalez-Pinto has received grants and served as consultant, advisor, or CME speaker for the following entities: Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Alter, Angelini, Novartis, Rovi, Takeda, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (CIBERSAM), the Ministry of Science (Carlos III Institute), the Basque Government, and the European Framework Program of Research. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). Arlington. 2013
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

