Unraveling molecular interconnections and identifying potential therapeutic targets of significance in obesity-cancer link
- PMID: 40040878
- PMCID: PMC11873641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jncc.2024.11.001
Unraveling molecular interconnections and identifying potential therapeutic targets of significance in obesity-cancer link
Abstract
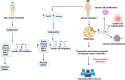
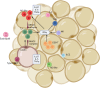
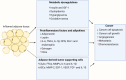
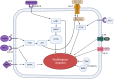
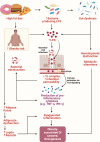
Obesity, a global health concern, is associated with severe health issues like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory complications. It also increases the risk of various cancers, including melanoma, endometrial, prostate, pancreatic, esophageal adenocarcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, renal adenocarcinoma, and pre-and post-menopausal breast cancer. Obesity-induced cellular changes, such as impaired CD8+ T cell function, dyslipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, insulin resistance, mild hyperglycemia, and fluctuating levels of leptin, resistin, adiponectin, and IL-6, contribute to cancer development by promoting inflammation and creating a tumor-promoting microenvironment rich in adipocytes. Adipocytes release leptin, a pro-inflammatory substance that stimulates cancer cell proliferation, inflammation, and invasion, altering the tumor cell metabolic pathway. Adiponectin, an insulin-sensitizing adipokine, is typically downregulated in obese individuals. It has antiproliferative, proapoptotic, and antiangiogenic properties, making it a potential cancer treatment. This narrative review offers a comprehensive examination of the molecular interconnections between obesity and cancer, drawing on an extensive, though non-systematic, survey of the recent literature. This approach allows us to integrate and synthesize findings from various studies, offering a cohesive perspective on emerging themes and potential therapeutic targets. The review explores the metabolic disturbances, cellular alterations, inflammatory responses, and shifts in the tumor microenvironment that contribute to the obesity-cancer link. Finally, it discusses potential therapeutic strategies aimed at disrupting these connections, offering valuable insights into future research directions and the development of targeted interventions.
Keywords: Cancer risk; Gut microbiome; Inflammation; Obesity; Therapeutic interventions; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024 Chinese National Cancer Center. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Swift D.L., McGee J.E., Earnest C.P., Carlisle E., Nygard M., Johannsen N.M. The effects of exercise and physical activity on weight loss and maintenance. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;61:206–213. - PubMed
-
- Apovian C.M. Obesity: definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am J Manag Care. 2016;22:s176–s185. - PubMed
-
- WHO; Organization WH. Obesity; 2024.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

