The lung proteome in HIV-associated obstructive lung disease
- PMID: 40040889
- PMCID: PMC11874292
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00204-2024
The lung proteome in HIV-associated obstructive lung disease
Abstract
Rationale: Obstructive lung disease is increasingly common among persons living with HIV (PLWH). There are currently no validated biomarkers that identify individuals at risk of developing obstructive lung disease (OLD), and specific mechanisms contributing to HIV-associated OLD remain elusive, independent of smoking. We sought to identify biomarkers and biological pathways associated with OLD using a broad proteomic approach.
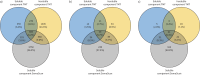
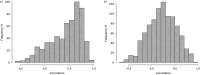
Methods: We performed tandem mass tagging and mass spectrometry (MS) analysis on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from persons living with HIV with OLD (n=26) and without OLD (n=26). We combined untargeted MS with a targeted SomaScan aptamer-based approach. We used Pearson correlation tests to identify associations between each protein and lung function (forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) % pred). We adjusted for multiple comparisons using a false discovery rate adjustment. Significant proteins were entered into a pathway over-representation analysis. Protein-driven endotypes were constructed using K-means clustering.
Measurements and main results: We identified over 3800 proteins by MS and identified 254 proteins that correlated with FEV1 % pred when we combined the MS and SomaScan proteomes when adjusting for smoking status. Pathway analysis revealed cell adhesion molecules as significant.
Conclusions: Protein expression differs in the lung of PLWH and decreased lung function (FEV1 % pred). Pathway analysis reveals cell adhesion molecules having potentially important roles in this process.
Copyright ©The authors 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: S. Samorodnitsky reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1. Conflict of interest: D. Weise reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1; and support for attending meetings and/or travel from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: E.F. Lock reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1. Conflict of interest: K.M. Kunisaki reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1; consulting fees from Allergan, outside the submitted work; participation in data safety monitoring board for Nuvaira and Organicell, outside the submitted work; and is a volunteer for the American Thoracic Society Proposal Review Committee, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: A. Morris reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1. Conflict of interest: J.M. Leung reports support for the present manuscript from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and BC Lung Foundation; grants or contracts from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and BC Lung Foundation, outside the submitted work; payment received from the BC Lung Foundation for patient forums, outside the submitted work; payment received from the University of British Columbia for education lectures, outside the submitted work; participation in the Enhance Quality Safety and Patient Experience in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder Data and Safety Monitoring Board, outside the submitted work; and is a member of the steering committee for Canadian Respiratory Research Network and CanCOLD Study, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: M. Kruk reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1; and support for attending meetings and/or travel from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: L. Parker reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1. Conflict of interest: P. Jagtap reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1. Conflict of interest: T.J. Griffin reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1. Conflict of interest: C.H. Wendt reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A1; support for attending meetings and/or travel from National Institutes of Health grant R01 HL140971-01A, outside the submitted work; and participation on a data and safety monitoring board for the Alpha1 Biomarkers Consortium and NIH, outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
