Macrophage expression of constitutively active TβRI alleviates hepatic injury in a mouse model of concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis
- PMID: 40040984
- PMCID: PMC11876931
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42691
Macrophage expression of constitutively active TβRI alleviates hepatic injury in a mouse model of concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis
Abstract
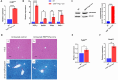
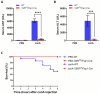
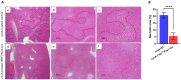
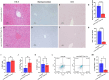
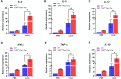
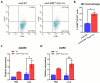
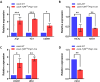
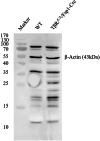
Transforming growth factor-β (Tgf-β) contributes to the development of liver diseases through its regulation of various cell types. While Tgf-β signaling to hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and hepatocytes was shown to mediate hepatic damage, the effect of Tgf-β on other cells in liver is yet to be clearly defined. Herein we identified a regulatory function of macrophage Tgf-β signaling in liver injury. We found that transgenic mice expressing constitutively active Tgf-β receptor type I (TβRI CA ) under the control of Fsp1-Cre (TβRI CA /Fsp1-Cre mice) were less susceptible to concanavalin A (conA)-induced autoimmune hepatitis. Liver tissue examination showed a decrease of necrotic area in conA-treated TβRI CA /Fsp1-Cre liver compared to those of wild-type mice. Blood test revealed that serum aminotransferases were significantly reduced in conA-treated TβRI CA /Fsp1-Cre mice as compared to those of wild-type mice. Immunohistochemistry for CD3 and myeloperoxidase demonstrated that there was a decreased accumulation of T cells and neutrophils, respectively, whereas ELISA showed that IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12 and IFN-γ was increased in livers of conA-treated TβRI CA /Fsp1-Cre mice. Alternatively activated macrophage (M2) polarization was significantly elevated in livers of conA-treated TβRI CA /Fsp1-Cre mice as indicated by enhanced hepatic expression of CCR2 and CD206 as well as increased numbers of liver macrophages expressing M2 subtype marker, CD163. qPCR analysis indicated an increased expression of TβRI CA , Arg1, Ym1, CD206, Snail1, Foxo1 and IRF4 as well as a decreased expression of MHC class II and CD1d in liver macrophages that were isolated from TβRI CA /Fsp1-Cre mice. Moreover, flow cytometry analysis showed a lower number of NKT cells in livers of conA-treated TβRI CA /Fsp1-Cre mice when compared to those of wild-type mice. In conclusion, Fsp1-Cre-mediated expression of TβRI CA lead to a decreased conA-induced liver injury that was associated with enhanced M2 macrophage polarization and reduced NKT cell recruitment.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

