Simultaneous Reversal of T Lymphocytes and Cancer Cells Metabolism Via a Biomimetic Heavy-Atom-Free Photosensitizers-Based Combination Therapies to Boost Cancer Photoimmunotherapy
- PMID: 40042072
- PMCID: PMC12021059
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202416143
Simultaneous Reversal of T Lymphocytes and Cancer Cells Metabolism Via a Biomimetic Heavy-Atom-Free Photosensitizers-Based Combination Therapies to Boost Cancer Photoimmunotherapy
Abstract
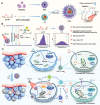
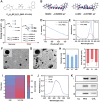
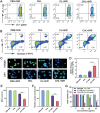
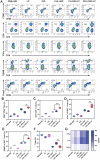
Near-infrared (NIR) activated photosensitizers based on heavy-atom-free have great advantages in photoimmunotherapy, yet the tumor microenvironment often restricts their efficacy. To address this, a NIR-activated heavy-atom-free photosensitizer (named Cy-BF) is developed. Cy-BF is then encapsulated with phospholipids and platelet exosome vesicles to create platelet exosomes vesicles biomimetic and Cy-BF loaded hybrid liposomes (named CHL) Characterized by high phototoxicity, low dark toxicity, and enhanced tumor targeting, CHL demonstrates aggregation-induced broadening of absorption spectra and NIR (760 nm laser) activates photothermal therapy and type I photodynamic therapy. The CHL-mediated phototherapy induces mitochondrial damage and immunogenic cell death in tumor cells, decreases lactate production, and alters the tumor microenvironment by reducing regulatory T cells and increasing CD8+ T cells. To mitigate T cell inhibition by excess lactate, a combination therapy is introduced using lithium carbonate, which repurposes lactate as an energy source for CD8+ T cells, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of CHL-mediated photoimmunotherapy. This combination approach represents a novel strategy for reversing lactate metabolism in both tumor cells and T cells, paving the way for future clinical applications in photoimmunotherapy.
Keywords: NIR activated type I/II PDT; T lymphocytes and cancer cells metabolism; heavy‐atom‐free photosensitizer; lithium carbonate; photoimmunotherapy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- a) Hu F., Xu S., Liu B., Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801350; - PubMed
- b) Wang K., Li Y., Wang X., Zhang Z., Cao L., Fan X., Wan B., Liu F., Zhang X., He Z., Zhou Y., Wang D., Sun J., Chen X., Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2950; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Zhu D., Duo Y., Meng S., Zhao Y., Xia L., Zheng Z., Li Y., Tang B. Z., Angew. Chem. 2020, 59, 2. - PubMed
-
- a) Ning S., Lyu M., Zhu D., Lam J. W. Y., Huang Q., Zhang T., Tang B. Z., ACS Nano 2023, 17, 10206; - PubMed
- b) Zhu D., Zheng Z., Luo G., Suo M., Li X., Duo Y., Tang B. Z., Nano Today 2021, 37, 101091;
- c) Wang X., Sun W., Shi H., Ma H., Niu G., Li Y., Zhi J., Yao X., Song Z., Chen L., Li S., Yang G., Zhou Z., He Y., Qu S., Wu M., Zhao Z., Yin C., Lin C., Gao J., Li Q., Zhen X., Li L., Chen X., Liu X., An Z., Chen H., Huang W., Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5091; - PMC - PubMed
- d) Zhu D., Zhang T., Li Y., Huang C., Suo M., Xia L., Xu Y., Li G., Tang B. Z., Biomaterials 2022, 283, 121462. - PubMed
-
- a) Ning S., Suo M., Huang Q., Gao S., Qiao K., Lyu M., Huang Q., Zhang T., Tang B. Z., Nano Today 2024, 54, 102106;
- b) Chen Z., Liu Z., Zhou Y., Rao K., Lin J., Zhu D., Ning S., Wang H., Mater.Today Bio 2024, 28, 101217; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Ning S., Zhang X., Suo M., Lyu M., Pan Y., Jiang Y., Yang H., Yip Lam J. W., Zhang T., Pan L., Tang B. Z., Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101505;
- d) Chen Q., Hu Q., Dukhovlinova E., Chen G., Ahn S., Wang C., Ogunnaike E. A., Ligler F. S., Dotti G., Gu Z., Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900192. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82303797/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82473348/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82403336/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- NUHSRO/2020/133/Startup/08/National University of Singapore
- NUHSRO/2023/008/NUSMed/TCE/LOA/National University of Singapore
- NUHSRO/2021/034/TRP/09/Nanomedicine/National University of Singapore
- 23-0173-A0001/National University of Singapore
- MOH-001388-00/National Medical Research Council
- CG21APR1005/National Medical Research Council
- MOH-001500-00/National Medical Research Council
- MOH-001609-00/National Medical Research Council
- MOE-000387-00/Singapore Ministry of Education
- MOET32023-0005/Singapore Ministry of Education
- NRF-000352-00/National Research Foundation
- BX20240233/China National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents
- HYDSYYXQN2023002/Excellent youth project of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University
- YQJH2024135/Basic research support program for Outstanding Young teachers of Universities in Heilongjiang Province
- PL2024H151/Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
