SERS-Based Assessment of DNA Methylation for the Evaluation of Measurable Residual Disease in Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia
- PMID: 40042091
- PMCID: PMC11880916
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70244
SERS-Based Assessment of DNA Methylation for the Evaluation of Measurable Residual Disease in Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia
Abstract
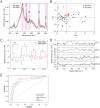
Acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APL) is a type of acute myeloid leukaemia characterised by the reciprocal translocation t(15;17), which offers a unique possibility for measurable residual disease (MRD) monitoring by PCR amplification of the PML-RARA transcripts. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is a laser molecular spectroscopy technique that allows the rapid analysis of changes in the DNA methylation pattern associated with malignant transformation. In this study involving 49 DNA samples from bone marrow aspirations from patients with APL, we showed that the DNA from MRD-positive samples exhibited lower SERS intensities of the band at 730 cm-1 attributed to adenine. Next, we used the scores derived from principal component analysis (PCA) as input data for machine learning algorithms trained to categorise SERS spectra based on MRD status. The results showed that the highest classification accuracy was achieved by logistic regression, yielding an area under the ROC curve (AUROC) of 0.90. In addition, PCA showed that samples corresponding to patients with FLT3-ITD mutations had a tendency for unsupervised clustering irrespective of MRD status. These results suggest that SERS analysis of DNA represents a promising method for the MRD monitoring of APL patients. Future validation of these findings in large prospective studies is warranted.
Keywords: SERS; acute promyelocytic leukaemia; minimal residual disease.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ten Cate H. and Leader A., “Management of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Acute Leukemias,” Hämostaseologie 41, no. 2 (2021): 120–126. - PubMed
-
- Burnett A. K., Russell N. H., Hills R. K., et al., “Arsenic Trioxide and All‐Trans Retinoic Acid Treatment for Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia in all Risk Groups (AML17): Results of a Randomised, Controlled, Phase 3 Trial,” Lancet Oncology 16, no. 13 (2015): 1295–1305. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

