Dietary oxidized lipids in redox biology: Oxidized olive oil disrupts lipid metabolism and induces intestinal and hepatic inflammation in C57BL/6J mice
- PMID: 40043451
- PMCID: PMC11927754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103575
Dietary oxidized lipids in redox biology: Oxidized olive oil disrupts lipid metabolism and induces intestinal and hepatic inflammation in C57BL/6J mice
Abstract
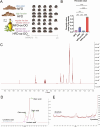
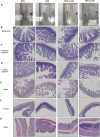
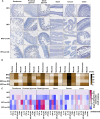
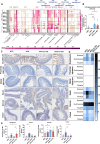
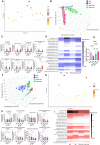
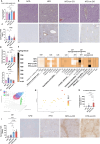
Olive oil, rich in oleic acid, is often regarded as a healthier alternative to animal fats high in saturated fatty acids and plant oils rich in oxidizable polyunsaturated fatty acids. However, the redox biological implications and health effects of oxidized olive oil (ox-OO) remain underexplored. Our study investigated its impact on lipid metabolism, intestinal and hepatic inflammation, and gut microbiota. Female C57BL/6J mice were fed either a standard normal (NFD), high-fat diet (HFD), an NFD-ox-OO or HFD-ox-OO, in which ox-OO (180 °C heating, 10 min) was the sole lipid source. Inflammation was assessed using macrophage marker F4/80 immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. Gene expression of inflammatory and lipid metabolism markers (IL-10, NF-kBp65, IL-1β, TNFα, TLR4, COX2, PPARα, PPARγ, CPT1a, SCAD, MCAD, LCAD) was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) protein expression was measured using IHC. Oxylipin and carnitine profiles were determined by LC-MS/MS. Gut microbiota was analyzed by 16S rRNA sequencing. Ox-OO disrupted redox homeostasis, leading to lipid metabolic dysfunction in the intestines and liver. In the duodenum and proximal jejunum, ox-OO decreased the levels of anti-inflammatory oxylipins and increased pro-inflammatory mediators, leading to inflammation. In the ileum and colon, ox-OO caused lipid metabolic dysregulation and inflammation. Colon inflammation was linked to inhibited mitochondrial β-oxidation and decreased short-chain fatty acid-producing microbiomes. Notably, redox imbalances were further implicated by the identification of 9,10-epoxy-stearic acid, a novel inflammatory lipid mediator oxidized from dietary oleic acid, which upregulated sEH. Ox-OO affects lipid metabolism and may contribute to inflammation in the gut and liver, raising questions about the assumption that olive oil is always beneficial and suggesting possible risks linked to oxidized oleic acid.
Keywords: 9,10-Epoxy-stearic acid; Gut microbiota; Inflammation; Lipid metabolic dysfunction; Oxidized olive oil.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Dyall S.C., Balas L., Bazan N.G., Brenna J.T., Chiang N., da Costa Souza F., Dalli J., Durand T., Galano J.M., Lein P.J., Serhan C.N., Taha A.Y. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and fatty acid-derived lipid mediators: recent advances in the understanding of their biosynthesis, structures, and functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022;86 doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang W., Wang Y., Sanidad K., Zhang J., Yang H., Johnson D., Sherman H., Kim D., Minter L., Decker E., Zhang G. Oxidized linoleic acid interacts with gut microbiota to promote colitis and colorectal cancer. Research Square. 2021
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

