Structure-function relationship of ASH1L and histone H3K36 and H3K4 methylation
- PMID: 40044670
- PMCID: PMC11883000
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57556-5
Structure-function relationship of ASH1L and histone H3K36 and H3K4 methylation
Abstract
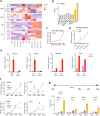
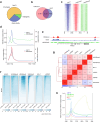
The histone H3K36-specific methyltransferase ASH1L plays a critical role in development and is frequently dysregulated in human diseases, particularly cancer. Here, we report on the biological functions of the C-terminal region of ASH1L encompassing a bromodomain (ASH1LBD), a plant homeodomain (ASH1LPHD) finger, and a bromo-adjacent homology (ASH1LBAH) domain, structurally characterize these domains, describe their mechanisms of action, and explore functional crosstalk between them. We find that ASH1LPHD recognizes H3K4me2/3, whereas the neighboring ASH1LBD and ASH1LBAH have DNA binding activities. The DNA binding function of ASH1LBAH is a driving force for the association of ASH1L with the linker DNA in the nucleosome, and the large interface with ASH1LPHD stabilizes the ASH1LBAH fold, merging two domains into a single module. We show that ASH1L is involved in embryonic stem cell differentiation and co-localizes with H3K4me3 but not with H3K36me2 at transcription start sites of target genes and genome wide, and that the interaction of ASH1LPHD with H3K4me3 is inhibitory to the H3K36me2-specific catalytic activity of ASH1L. Our findings shed light on the mechanistic details by which the C-terminal domains of ASH1L associate with chromatin and regulate the enzymatic function of ASH1L.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL151334/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 AG072562/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM152184/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA239165/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA080058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM126900/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA252707/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- AG067664/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- S10 OD028504/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI177461/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

