Effects of intra-articular applied rat BMSCs expressing alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide or substance P on osteoarthritis pathogenesis in a murine surgical osteoarthritis model
- PMID: 40045368
- PMCID: PMC11884178
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-025-04155-2
Effects of intra-articular applied rat BMSCs expressing alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide or substance P on osteoarthritis pathogenesis in a murine surgical osteoarthritis model
Abstract
Background: About 655 million persons worldwide are affected by osteoarthritis (OA). As no therapy modifies disease progression long-term, there is an immense clinical need for novel therapies. The joints are innervated by alpha calcitonin gene-related peptide (αCGRP)- and substance P (SP)-positive sensory nerve fibers. Both neuropeptides have trophic effects on target cells within the joints. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of SP- and αCGRP-expressing intra-articular (i.a.) applied rat(r)BMSC on cartilage and subchondral bone structural changes after OA induction.
Methods: Mice were subjected to destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) surgery, followed by i.a. injections with rBMSC, transduced with lacZ, SP or αCGRP. 2, 8 and 16 weeks after DMM/Sham surgery, motion analysis and serum marker analysis were performed. Cartilage and subchondral bone properties were assessed by OA scoring, atomic force microscopy and nano-CT analysis.
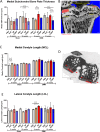
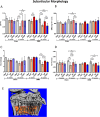
Results: OARSI scores of the medial cartilage compartments indicated induction and progression of OA after DMM surgery in all groups. Differences between the treatment groups were mostly restricted to the lateral cartilage compartments, where αCGRP caused a decrease of structural changes. DMM-rBMSC-αCGRP or -SP mice displayed decreased cartilage stiffness in the cartilage middle zone. DMM-rBMSC-αCGRP mice revealed improved mobility, whereas Sham-rBMSC-SP mice revealed reduced mobility compared to rBMSC-lacZ. With respect to condyle length, subarticular bone and ephiphyseal bone morphology, DMM-rBMSC-SP mice had more alterations indicating either a more progressed OA stage or a more severe OA pathology compared to controls. In addition, DMM-rBMSC-SP mice developed osteophytes already 8 weeks after surgery. Adiponectin serum level was increased in DMM-rBMSC-αCGRP mice, and MIP1b level in DMM-rBMSC-SP mice. Notably, pain and inflammation markers increased over time in rBMSC-SP mice while rBMSC-αCGRP mice revealed a bell-shaped curve with a peak at 8 weeks.
Conclusions: We conclude that i.a. injection of rBMSC in general have a beneficial effect on cartilage matrix structure, subchondral bone microarchitecture and inflammation. rBMSC-αCGRP have anabolic and possible analgesic properties and may attenuate the progression or severity of OA. In contrast, rBMSC-SP exert a more catabolic influence on knee joints of both, Sham and DMM mice, making it a potential candidate for inhibition studies.
Keywords: AFM; BMSC; DMM; Motion analysis; Nanoct; Osteoarthritis; SP; Serum marker; αCGRP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Title of the project: Der Einfluss des sensiblen Nervensystems (SP- und alphaCGRP-positive Nervenfasern) auf die OA Pathogenese. The local authorities in Würzburg (Regierung von Unterfranken) approved all animal experiments. Approval number: AZ 55.2-2532-2-306. Date of approval: 15th of September 2016. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Usage of AI: The authors declare that they have not used Artificial Intelligence in this study. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthr Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745–59. - PubMed
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Nolte S, Ackerman I, Fransen M, Bridgett L, Williams S, Guillemin F, Hill CL, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323–30. - PubMed
-
- Diduch DR, Crawford DC, Ranawat AS, Victor J, Flanigan DC. Implantable shock Absorber provides Superior Pain Relief and functional improvement compared with high tibial osteotomy in patients with mild-to-moderate medial knee osteoarthritis: a 2-Year report. Cartilage. 2023;14(2):152–63. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

