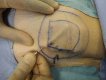
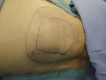
Autologous fat grafting for management of pain at spinal cord implantable pulse generator sites
- PMID: 40045949
- PMCID: PMC11880733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra.2024.06.019
Autologous fat grafting for management of pain at spinal cord implantable pulse generator sites
Abstract
Implantable pulse generator site pain is prevalent in 4 to 12 percent of patients with the spinal cord stimulators. We have used a case series of 4 patients aged 46 to 79, to demonstrate pain relief at the implant site via the use of autologous fat grafting. All patients experienced an improvement of 33.3 % to 75 % in pain scores within a few weeks of the procedure. Up to a 21 month follow up date, there was still pain relief with no complications. Subsequently, we propose that autologous fat grafting may be effective and safe in pain management at the implant pulse generator sites. Further studies with larger case series and long term follow up is needed for validation.
Keywords: Fat grafting; Implantable pulse generator; Pain.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Atkinson L., Sundaraj S.R., Brooker, et al. Recommendations for patient selection in spinal cord stimulation. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:1295–1302. - PubMed
-
- Hayek S.M., Veizi E., Hanes M. Treatment-limiting complications of percutaneous spinal cord stimulator implants: a review of eight years of experience from an academic center database. Neuromodulation. 2015;18:603–608. - PubMed
-
- Mekhail NA, Mathews M, Nageeb F, et al. Retrospective review of 707 cases of Spinal cord stimulation: indications and complications. Pain Pract. 2011;11(2):148–153. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources