Tau levels in platelets isolated from Huntington's disease patients serve as a biomarker of disease severity
- PMID: 40047995
- PMCID: PMC11885373
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-025-12966-9
Tau levels in platelets isolated from Huntington's disease patients serve as a biomarker of disease severity
Abstract
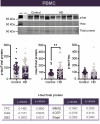
Tau is a microtubule protein that is known to be hyperphosphorylated and to aggregate in several chronic neurodegenerative disorders. In many cases, in particular in Alzheimer's disease, the degree of tau pathology has been demonstrated to correlate with cognitive deficits and/or decline. In Huntington's disease (HD), a dominantly inherited neurodegenerative disorder, both cognitive impairments and abnormal tau expression have been reported to occur, along with the accumulation of the mutant huntingtin protein. In this respect, tau has been shown to be present in the cerebrospinal fluid of individuals with HD and to increase with disease progression. However, how this relates to changes in tau found in the periphery is largely unknown. In this study, we collected blood samples from patients with HD and isolated multiple blood components including plasma, platelets, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells to measure their tau levels and subsequently correlate these to cognitive impairments and disease stage. Our results suggest that the amount of tau, particularly N-terminal tau (NTA-tau) and total tau (t-tau), is elevated in all assayed blood components and that the quantity of tau within platelets, specifically, is strongly correlated with disease severity.
Keywords: Blood; Cognition; NTA-tau; PBMC; Phosphorylated tau; Plasma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: KB has served as a consultant and at advisory boards for Acumen, ALZPath, BioArctic, Biogen, Eisai, Julius Clinical, Lilly, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers; has served at data monitoring committees for Julius Clinical and Novartis; has given lectures, produced educational materials and participated in educational programs for AC Immune, Biogen, Celdara Medical, Eisai, and Roche Diagnostics; and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this paper. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. HZ has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZpath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Enigma, LabCorp, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Quanterix, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures sponsored by Alzecure, BioArctic, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche, and WebMD, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). FC is a co-founder of Synucure Therapeutics and a consultant for Axoltis and HD immune Vienna. RAB is on the editorial board of the Journal of Neurology.
Figures


References
-
- Devi G (2023) The tauopathies. Handb Clin Neurol 196:251–265. 10.1016/B978-0-323-98817-9.00015-6 - PubMed
-
- Riemenschneider M, Wagenpfeil S, Vanderstichele H et al (2003) Phospho-tau/total tau ratio in cerebrospinal fluid discriminates Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease from other dementias. Mol Psychiatry 8:343–347. 10.1038/sj.mp.4001220 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZEN-21-848495/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- ALZ2022-0006/Hjärnfonden
- 2023-00356/Vetenskapsrådet
- 2019-02397/Vetenskapsrådet
- AF-968270/Alzheimerfonden
- ADSF-21-831376-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- 2022-01018/Vetenskapsrådet
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- ADSF-21-831377-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- 2017-00915/Vetenskapsrådet
- AF-930351/Alzheimerfonden
- ALFGBG-965240/Vetenskapsrådet
- 201809-2016862/Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation
- ALFGBG-715986/Vetenskapsrådet
- FO2017-0243/Hjärnfonden
- #22HLT07/European Partnership on Metrology
- JPND2019-466-236/EU Joint Programme - Neurodegenerative Disease Research
- SG-23-1038904 QC/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- ADSF-21-831381-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- ALFGBG-71320/Vetenskapsrådet
- 860197/HORIZON EUROPE Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions
- JPND2021-00694/EU Joint Programme - Neurodegenerative Disease Research
- AF-939721/Alzheimerfonden
- 2022-00732/Vetenskapsrådet
- UKDRI-1003/UK Dementia Research Institute
- 101053962/European Union's Horizon Europe research and innovation programme
- FO2022-0270/Hjärnfonden
- ADSF-24-1284328-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

