Preclinical Evaluation of 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1, a Radiopharmaceutical for Prostate Cancer: Biodistribution and Therapeutic Efficacy
- PMID: 40049746
- PMCID: PMC11960612
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268508
Preclinical Evaluation of 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1, a Radiopharmaceutical for Prostate Cancer: Biodistribution and Therapeutic Efficacy
Abstract
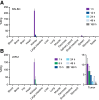
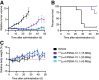
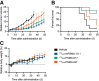
177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 is a novel radiohybrid prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy for prostate cancer. We conducted preclinical analyses on non-tumor-bearing BALB/c mice and on prostate cancer human xenograft mouse models (LNCAP and 22Rv1 xenografts) to evaluate its biodistribution and therapeutic efficacy. Methods: Longitudinal biodistribution of 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 was evaluated in BALB/c mice and 22Rv1 xenografts. Tissues of interest were harvested, and radioactivity was measured 1-168 h after injection of 1 MBq of 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 (4 per time point). Longitudinal biodistribution was compared with 177Lu-PSMA-I&T (1 MBq) in BALB/c mice and at a single time point (15 h) in 22Rv1 xenografts. The therapeutic efficacy of a single administration of 15, 30, or 45 MBq of 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 in LNCaP xenografts and 30 MBq of 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1, 177Lu-PSMA-617, or 177Lu-PSMA-I&T in 22Rv1 xenografts (8 per group) was evaluated. Efficacy versus vehicle was evaluated on the basis of relative tumor volume and survival up to 49 d after administration. Statistical significance was evaluated with t testing (biodistribution data), 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA (tumor volume [analyzed until 3 per group remained]), or Kaplan-Meier log-rank analyses (survival). Results: Biodistribution of 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 in the BALB/c and 22Rv1 xenografts showed rapid clearance from blood and other normal tissues within 48 h, with the kidney showing the highest normal-organ uptake. Kidney uptake and retention were lower for 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 than for 177Lu-PSMA-I&T (6.5-fold lower at 12 h in BALB/c mice and 6.4-fold lower at 15 h in 22Rv1 xenografts; P < 0.01). High and sustained 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 tumor uptake was observed in 22Rv1 xenografts. This uptake was 2.3-fold higher than that of 177Lu-PSMA-I&T (15 h; P < 0.05). When efficacy was evaluated, 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 significantly suppressed tumor growth versus vehicle from day 11 (P < 0.05) in LNCaP xenografts in a dose-dependent manner and from day 18 (P < 0.05) in 22Rv1 xenografts and significantly prolonged median survival versus vehicle in both models. In 22Rv1 xenografts, 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 suppressed tumor growth versus vehicle to a greater extent than did 177Lu-PSMA-I&T (significant growth inhibition from day 25 [P < 0.05]) and similarly in extent to 177Lu-PSMA-617 (from day 18 [P < 0.05]). Overall, compared with 177Lu-PSMA-I&T, 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 suppressed tumor growth for longer than 177Lu-PSMA-617 (inhibition from day 39 onward [P < 0.05] versus on day 49 only [P < 0.05]). Conclusion: In preclinical models, 177Lu-rhPSMA-10.1 shows a favorable tumor-to-kidney uptake ratio, and significant antitumor effects, indicating it to be a promising next-generation radiopharmaceutical therapy.
Keywords: PSMA; biodistribution; preclinical; prostate cancer; radiopharmaceutical.
© 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Heck MM, Tauber R, Schwaiger S, et al. . Treatment outcome, toxicity, and predictive factors for radioligand therapy with 177Lu-PSMA-I&T in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2019;75:920–926. - PubMed
-
- Hofman MS, Violet J, Hicks RJ, et al. . [177Lu]-PSMA-617 radionuclide treatment in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (LuPSMA trial): a single-centre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:825–833. - PubMed
-
- Demirkol M, Esen B, Sen M, et al. . Radioligand therapy with 177Lu-PSMA-I&T in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: oncological outcomes and toxicity profile. J Urol. 2023;209:e125. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
