SART3 promotes homologous recombination repair by stimulating DNA-RNA hybrids removal and DNA end resection
- PMID: 40050279
- PMCID: PMC11885473
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57599-8
SART3 promotes homologous recombination repair by stimulating DNA-RNA hybrids removal and DNA end resection
Abstract
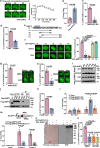
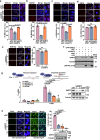
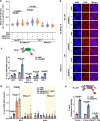
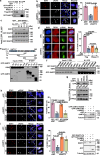
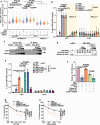
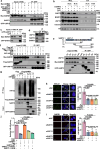
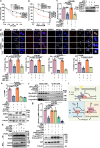
DNA-RNA hybrids triggered by double-strand breaks (DSBs) are crucial intermediates during DSB repair, and their timely resolution requires numbers of RNA helicases, including DEAD box 1 (DDX1). However, how these helicases are recruited to DSB-induced hybrids in time remains largely unclear. Here, we revealed that squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T cells 3 (SART3) promotes DDX1 binding to DNA-RNA hybrids at DSBs for optimal homologous recombination (HR) repair. SART3 itself associates with DNA-RNA hybrids and PAR chains and accumulates at DSBs in both PARylation- and DNA-RNA hybrids-dependent fashion. SART3 also associates with DDX1 and is necessary for DDX1 enrichment at DSBs. The defective SART3-DDX1 association observed in cells expressing the cancer-associated variant SART3-R836W impairs not only the accumulation of DDX1, but also hybrid removal and HR efficiency. Moreover, SART3 promotes DNA end resection through enhancing USP15-BARD1 association and BRCA1-BARD1 retention. Together, our study reveals an role of SART3 in DSB repair, rendering SART3 a promising target for cancer therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

