Genetically-encoded markers for confocal visualization of single dense core vesicles
- PMID: 40050695
- PMCID: PMC11885565
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-07829-y
Genetically-encoded markers for confocal visualization of single dense core vesicles
Abstract
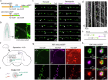
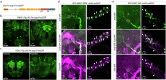
Neuronal dense core vesicles (DCVs) store and release a diverse array of neuromodulators, trophic factors, and bioamines. The analysis of single DCVs has largely been possible only using electron microscopy, which makes understanding cargo segregation and DCV heterogeneity difficult. To address these limitations, we develop genetically encoded markers for DCVs that can be used in combination with standard immunohistochemistry and expansion microscopy to enable single-vesicle resolution with confocal microscopy in Drosophila.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Genetically-encoded markers for confocal visualization of single dense core vesicles.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 8:2024.10.07.617131. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.07.617131. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 07;8(1):383. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07829-y. PMID: 39416146 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Genetically-encoded markers for confocal visualization of single dense core vesicles.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 21:rs.3.rs-5021271. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5021271/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 07;8(1):383. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07829-y. PMID: 39502772 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Edwards, R. H. Neurotransmitter release: variations on a theme. Curr. Biol.8, R883–885 (1998). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

