Circular RNA circCLASP2 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through binding to DHX9 to enhance PCMT1 translation
- PMID: 40050914
- PMCID: PMC11884054
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02272-3
Circular RNA circCLASP2 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through binding to DHX9 to enhance PCMT1 translation
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs), characterized by their covalently closed-loop structures, constitute a distinct class of non-coding RNAs. They play pivotal regulatory roles within cells and are intricately associated with the progression of malignant tumors. However, their roles and the underlying mechanisms in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) progression have yet to be fully uncovered and comprehensively understood.
Methods: Employing RNA sequencing technology, high-abundance circular RNAs in NPC were identified. Expression analysis of circCLASP2 in NPC tissues was conducted using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and in situ hybridization experiments. Through in vitro and in vivo functional assays, the influence of circCLASP2 on the proliferation and metastasis of NPC was investigated. LC-MS/MS technology analyzed the binding partners of circCLASP2, its differentially regulated targets, and the associated proteins of PCMT1. Interactions among circCLASP2, DHX9 protein, and PCMT1 mRNA were elucidated through RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA pull-down techniques. The effects of circCLASP2 and DHX9 on RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) structures and PCMT1 mRNA translation were explored through immunofluorescence (IF), ribosomal gradient separation, and dual-luciferase reporter assays. Immunoprecipitation (IP) revealed the downstream effector of the circCLASP2-DHX9-PCMT1 regulatory axis and Phalloidin staining confirmed its ultimate effect on the cytoskeleton. PDS treatment was applied for interventions in NPC, demonstrating potential therapeutic avenues.
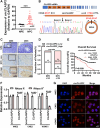
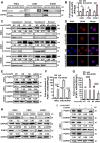
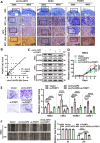
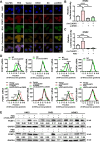
Results: Our research revealed that circCLASP2, a novel circRNA that has not been reported in tumors, is upregulated in NPC and fosters cell proliferation and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, circCLASP2 acts as a molecular scaffold, facilitating the approximation of DHX9 to PCMT1 mRNA. DHX9 unwinds the inhibitory rG4 structure near the translation initiation site on PCMT1 mRNA, increasing PCMT1 expression. PCMT1 binds to and upregulates cytoskeleton-associated proteins, modulating cytoskeleton strength and dynamics and ultimately driving NPC cell proliferation and metastasis. In both in vitro and in vivo experiments, PDS significantly inhibits NPC growth and metastasis, showcasing promising therapeutic potential.
Conclusions: Our investigation pinpointed a circular RNA, circCLASP2, which is upregulated in NPC and augments cytoskeletal functions via the DHX9-PCMT1 axis, contributing to the malignancy progression of NPC. This pathway holds promise as a potential therapeutic target for NPC. Furthermore, these molecules could also serve as biomarkers for adjunct diagnosis and prognosis assessment in NPC.
Keywords: CircCLASP2; Cytoskeleton; DHX9; Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma; PCMT1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Central South University. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wang D, Zuo S, Ge J, Qu H, Wu J, Yi N, et al. CircTP63-N suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via engaging with HSP90AB1 to modulate the YAP1/Hippo signaling pathway. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. 10.1007/s11427-023-2737-2. - PubMed
-
- Tu C, Zeng Z, Qi P, Li X, Guo C, Xiong F, et al. Identification of genomic alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived Epstein-Barr virus by whole-genome sequencing. Carcinogenesis. 2018;39:1517–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

