The genome sequence of the butterfly blenny, Blennius ocellaris Linnaeus, 1758
- PMID: 40051962
- PMCID: PMC11883214
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.23748.1
The genome sequence of the butterfly blenny, Blennius ocellaris Linnaeus, 1758
Abstract
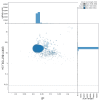
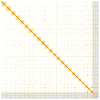
We present a genome assembly from a specimen of Blennius ocellaris (the butterfly blenny; Chordata; Actinopteri; Blenniiformes; Blenniidae). The genome sequence spans 728.70 megabases. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into 24 chromosomal pseudomolecules. The mitochondrial genome has also been assembled and is 16.5 kilobases in length.
Keywords: Blenniiformes; Blennius ocellaris; butterfly blenny; chromosomal; genome sequence.
Copyright: © 2025 Adkins P et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Bates A, Clayton-Lucey I, Howard C: Sanger Tree of Life HMW DNA fragmentation: diagenode Megaruptor ®3 for LI PacBio. protocols.io. 2023. 10.17504/protocols.io.81wgbxzq3lpk/v1 - DOI
-
- Beasley J, Uhl R, Forrest LL, et al. : DNA barcoding SOPs for the Darwin Tree of Life project. protocols.io. 2023; [Accessed 25 June 2024]. 10.17504/protocols.io.261ged91jv47/v1 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

