A maturity model for Clinical Trials Management Ecosystem
- PMID: 40052053
- PMCID: PMC11883580
- DOI: 10.1017/cts.2024.1168
A maturity model for Clinical Trials Management Ecosystem
Abstract
Introduction: Managing clinical trials is a complex process requiring careful integration of human, technology, compliance, and operations for success. We collaborated with experts to develop a multi-axial Clinical Trials Management Ecosystem (CTME) maturity model (MM) to help institutions identify best practices for CTME capabilities.
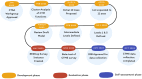
Methods: A working group of research informaticists was established. An online session on maturity models was hosted, followed by a review of the candidate domain axes and finalization of the axes. Next, maturity level attributes were defined for min/max levels (level 1 and level 5) for each axis of the CTME MM, followed by the intermediate levels. A REDCap survey comprising the model's statements was then created, and a subset of working group members tested the model by completing it at their respective institutions. The finalized survey was distributed to all working group members.
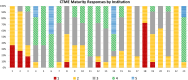
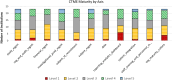
Results: We developed a CTME MM comprising five maturity levels across 11 axes: study management, regulatory and audit management, financial management, investigational product management, subject identification and recruitment, subject management, data, reporting analytics & dashboard, system integration and interfaces, staff training & personnel management, and organizational maturity and culture. Informaticists at 22 Clinical and Translational Science Award hubs and one other organization self-assessed their institutional CTME maturity. Respondents reported relatively high maturity for study management and investigational product management. The reporting analytics & dashboard axis was the least mature.
Conclusion: The CTME MM provides a framework to research organizations to evaluate their current clinical trials management maturity across 11 axes and identify areas for future growth.
Keywords: Clinical Trials Management Ecosystem; clinical and translational research; clinical trials; informatics; maturity models.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no relevant competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Aiwerioghene EM, Lewis J, Rea D. Maturity models for hospital management: a literature review. Int J Healthc Manag. 2024;1–14. doi: 10.1080/20479700.2024.2367858. - DOI
-
- Nolan Richard L. Managing the computer resource: a stage hypothesis. Commun ACM. 1973;16(7):399–405. doi: 10.1145/362280.362284. - DOI
-
- Paulk Mark, Curtis Bill, Chrissis Mary, Weber Charles. Capability maturity model, Version 1.1. IEEE Software. 1993;10(4):18–27. doi: 10.1109/52.219617. - DOI
-
- García-Mireles GA, Ángeles Moraga MÁ, García F. Development of maturity models: A systematic literature review. In: 16th International Conference on Evaluation & Assessment in Software Engineering (EASE 2012), Ciudad Real, 2012:279–283. doi: 10.1049/ic.2012.0036. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
