A novel nomogram based on complement C3 to predict the overall survival of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion-positive undergoing curative resection
- PMID: 40052130
- PMCID: PMC11882412
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1559083
A novel nomogram based on complement C3 to predict the overall survival of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion-positive undergoing curative resection
Abstract
Purpose: This investigation aimed to create a new nomogram based on complement C3 to forecast 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) exhibiting microvascular invasion (MVI) post-curative surgery.
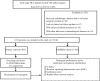
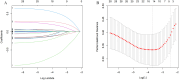
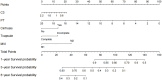
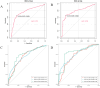
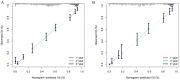
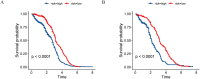
Methods: This study encompassed 1234 patients treated with resection at the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Guangxi Medical University. The cohort for primary included 865 patients from December 2015 to December 2019, while the validation cohort comprised 369 patients. Follow-ups were conducted regularly until December 2024. Variables predicting survival were identified using Cox regression analyses, and based on these, a nomogram was constructed. This nomogram's accuracy was assessed via time-dependent ROC curves, calibration curves and KM curve analyses.
Results: Investigations identified complement C3, PT, the presence of cirrhosis, tumor capsule, and MVI-M2 as distinct predictors of survival in HCC patients. Based on these findings, a predictive nomogram was constructed and validated, aimed at estimating the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS. The efficacy of the nomogram was validated through analyses with ROC curves, calibration curves, each demonstrating positive outcomes. Additionally, KM curve analysis effectively separated the patient populations into two prognostic risk categories within both the primary and validation cohorts.
Conclusion: In conclusion, a new nomogram has been developed and corroborated through multivariate Cox regression analysis, aimed at estimating overall survival for patients in early stages of microvascular invasion following surgical resection. This tool has proven to be more effective in forecasting survival outcomes for such patients post-curative surgery.
Keywords: curative resection; early-stage; hepatocellular carcinoma; microvascular invasion; overall survival.
Copyright © 2025 Xia, Yu, Lu, Wang, Zhao and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MRI Features and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR)-Based Nomogram to Predict Prognosis of Microvascular Invasion-Negative Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025 Feb 15;12:275-287. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S486955. eCollection 2025. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025. PMID: 39974612 Free PMC article.
-
Novel nomograms based on microvascular invasion grade for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 12;14(1):3470. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54260-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38342950 Free PMC article.
-
Lasso-Based Nomogram for Predicting Early Recurrence Following Radical Resection in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025 Mar 12;12:539-552. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S510581. eCollection 2025. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025. PMID: 40099228 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic nomogram based on microvascular invasion and hematological biomarkers to predict survival outcome for hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Surg Oncol. 2020 Jun;33:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2020.01.006. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32561099
-
Construction of web-based prediction nomogram models for cancer-specific survival in patients at stage IV of hepatocellular carcinoma depending on SEER database.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Oct 28;48(10):1546-1560. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.230040. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 38432884 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

