Cobalt-Embedded Metal-Covalent Organic Frameworks for CO2 Photoreduction
- PMID: 40053392
- PMCID: PMC11926853
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c18450
Cobalt-Embedded Metal-Covalent Organic Frameworks for CO2 Photoreduction
Abstract
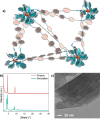
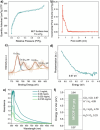
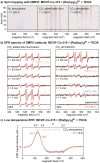
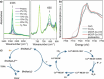
With the pressing urgency to reduce carbon footprint, photocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction has attracted growing attention as a sustainable mitigating option. Considering the important role of catalytic active sites (CASs) in the catalytic processes, control and design of the density and environment of CASs could enhance the catalyst performance. Herein, we report a novel metal-covalent organic framework (MCOF), MCOF-Co-315, featuring earth-abundant Co cocatalysts and conjugation through a covalently bonded backbone. MCOF-Co-315 showed a CO production rate of 1616 μmol g-1 h-1 utilizing Ru(bpy)3Cl2 as photosensitizer and triethanolamine (TEOA) as sacrificial electron donor with a 1.5 AM filter, vis mirror module (390-740 nm), and irradiation intensity adjusted to 1 sun and an especially outstanding apparent quantum yield (AQY) of 9.13% at 450 nm. The photocatalytic reaction was studied with electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy, X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES), and in situ synchrotron Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, and an underlying mechanism is proposed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wei Y.; Chen L.; Chen H.; Cai L.; Tan G.; Qiu Y.; Xiang Q.; Chen G.; Lau T.; Robert M. Highly efficient photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO by in situ formation of a hybrid catalytic system based on molecular iron quaterpyridine covalently linked to carbon nitride. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e20211683210.1002/anie.202116832. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

