Penalised regression improves imputation of cell-type specific expression using RNA-seq data from mixed cell populations compared to domain-specific methods
- PMID: 40053530
- PMCID: PMC11957391
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012859
Penalised regression improves imputation of cell-type specific expression using RNA-seq data from mixed cell populations compared to domain-specific methods
Abstract
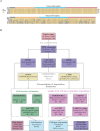
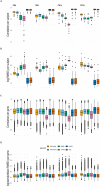
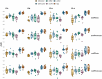
Gene expression studies often use bulk RNA sequencing of mixed cell populations because single cell or sorted cell sequencing may be prohibitively expensive. However, mixed cell studies may miss expression patterns that are restricted to specific cell populations. Computational deconvolution can be used to estimate cell fractions from bulk expression data and infer average cell-type expression in a set of samples (e.g., cases or controls), but imputing sample-level cell-type expression is required for more detailed analyses, such as relating expression to quantitative traits, and is less commonly addressed. Here, we assessed the accuracy of imputing sample-level cell-type expression using a real dataset where mixed peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and sorted (CD4, CD8, CD14, CD19) RNA sequencing data were generated from the same subjects (N=158), and pseudobulk datasets synthesised from eQTLgen single cell RNA-seq data. We compared three domain-specific methods, CIBERSORTx, bMIND and debCAM/swCAM, and two cross-domain machine learning methods, multiple response LASSO and ridge, that had not been used for this task before. We also assessed the methods according to their ability to recover differential gene expression (DGE) results. LASSO/ridge showed higher sensitivity but lower specificity for recovering DGE signals seen in observed data compared to deconvolution methods, although LASSO/ridge had higher area under curves than deconvolution methods. Machine learning methods have the potential to outperform domain-specific methods when suitable training data are available.
Copyright: © 2025 Lin et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: The CLUSTER consortium has been provided with generous grants from AbbVie and Sobi. CW receives funding from MSD and GSK and is a part-time employee of GSK. These companies had no involvement in the work presented here.
Figures



References
-
- Lyons PA, McKinney EF, Rayner TF, Hatton A, Woffendin HB, Koukoulaki M, et al.. Novel expression signatures identified by transcriptional analysis of separated leucocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(6):1208–13. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.108043 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

