Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Formulation Ru-Yi-Jin-Huang-Saan on Colles Fracture After Surgery: Protocol for a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40053806
- PMCID: PMC11923486
- DOI: 10.2196/56849
Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Formulation Ru-Yi-Jin-Huang-Saan on Colles Fracture After Surgery: Protocol for a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Colles fracture, a common wrist injury, often requires surgical intervention. After surgery, patients may experience persistent pain and reduced wrist function, potentially resulting in long-term disability. In clinical practice, traditional Chinese medicine practitioners frequently use Ru-Yi-Jin-Huang-Saan (RYJHS) to treat such patients in Taiwan. RYJHS is a traditional Chinese herbal formula with a history spanning centuries, primarily used topically for the treatment of bone fractures and the promotion of healing. However, there is currently a lack of substantial clinical evidence supporting its efficacy in the management of postsurgical Colles fractures. To the best of our knowledge, there are no studies evaluating the clinical effectiveness of RYJHS.
Objective: This study aims to investigate the therapeutic potential of RYJHS in postsurgical Colles fracture cases. An additional objective is to provide an alternative treatment option for postoperative patients unable to take anti-inflammatory and pain relief medications.
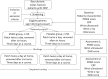
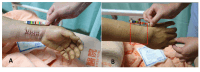
Methods: This is a protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. A total of 100 postoperative patients with Colles fracture, aged 20-80 years, will be recruited for this study. They will be randomly assigned to either the experimental or control group in a 1:1 allocation ratio. Both groups will receive standard postoperative Colles fracture treatment. The primary outcome measure will assess wrist functional recovery using the Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation score. Secondary outcomes will include C-reactive protein levels and ultrasound measurements of wrist swelling. All of these examinations will be assessed at baseline, 3 days after surgery, and 6 days after surgery. In addition, the Dyshidrotic Eczema Area and Severity Index will be used to monitor for adverse skin reactions.
Results: This protocol was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov on December 6, 2022. It was performed in accordance with the approved guidelines and regulations of the participating institutions. Recruitment began in May 2023, with data collection expected to conclude in May 2025. Study completion is expected in December 2025.
Conclusions: This is the first protocol discussing the assessment of the therapeutic efficacy and safety of topical traditional Chinese medicine in patients after fracture surgery. The protocol will establish an integrated care model combining both traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine for postsurgical fracture cases.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05638360; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05638360.
International registered report identifier (irrid): DERR1-10.2196/56849.
Keywords: Colles fracture; PRWE; PRWE score; Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation; RCT; Ru-Yi-Jin-Huang-Saan; Western medicine; alternative treatment; external application; fracture; pain relief medication; postoperative; protocol; randomized controlled trial; surgeries; traditional Chinese medicine; wrist evaluation.
©Lien-Cheng Lin, Wei-Hsun Wang, Wei-Kai Chang, Jyun-Liang Gao, Ru-Chang Yang, Po-Chi Hsu, Lun-Chien Lo. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (https://www.researchprotocols.org), 05.03.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Chung KC, Spilson SV. The frequency and epidemiology of hand and forearm fractures in the United States. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;26(5):908–915. doi: 10.1053/jhsu.2001.26322. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhsu.2001.26322 S0363-5023(01)93696-2 - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sebastin SJ, Chung KC. An Asian perspective on the management of distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2012;28(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2012.03.007. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22554658 S0749-0712(12)00015-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nellans KW, Kowalski E, Chung KC. The epidemiology of distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2012;28(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2012.02.001. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22554654 S0749-0712(12)00002-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raudasoja L, Aspinen S, Vastamäki H, Ryhänen J, Hulkkonen S. Epidemiology and treatment of distal radius fractures in Finland-a nationwide register study. J Clin Med. 2022;11(10):2851. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102851. https://www.mdpi.com/resolver?pii=jcm11102851 jcm11102851 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Handoll HHG, Elliott J. Rehabilitation for distal radial fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(9):CD003324. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003324.pub3. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/26403335 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

