Courtship song differs between African and European populations of Drosophila melanogaster and involves a strong effect locus
- PMID: 40053835
- PMCID: PMC12060230
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf050
Courtship song differs between African and European populations of Drosophila melanogaster and involves a strong effect locus
Abstract
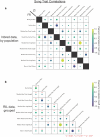
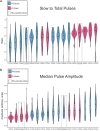
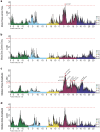
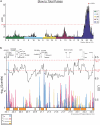
The courtship song of Drosophila melanogaster has long served as an excellent model system for studies of animal communication and differences in courtship song have been demonstrated among populations and between species. Here, we report that flies of African and European origin, which diverged ∼13,000 years ago, show significant genetic differentiation in the use of slow vs fast pulse song. Using a combination of quantitative trait mapping and population genetic analysis, we detected a single strong quantitative trait locus underlying this trait and we identified candidate genes that may contribute to the evolution of this trait. Song trait variation between parental strains of our recombinant inbred panel enabled detection of genomic intervals associated with 6 additional song traits, some of which include known courtship-related genes. These findings improve the prospects for further genetic insights into the evolution of reproductive behavior and the biology underlying courtship song.
Keywords: QTL mapping; behavior; courtship song; evolution; flyBase; variation.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Courtship song differs between African and European populations of Drosophila melanogaster and involves a strong effect locus.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 24:2024.05.14.594231. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.14.594231. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: G3 (Bethesda). 2025 May 8;15(5):jkaf050. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf050. PMID: 38798463 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Arthur BJ, Ding Y, Sosale M, Khalif F, Kim E, Waddell P, Turaga SC, Stern DL. 2021. Songexplorer: a deep learning workflow for discovery and segmentation of animal acoustic communication signals. bioRxiv 437280. 10.1101/2021.03.26.437280, preprint: not peer reviewed. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
