Expression of recombination antimicrobial protein PIL22-PBD-2 in Pichia pastoris and verification of its biological function in vitro
- PMID: 40055823
- PMCID: PMC11889930
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-024-01428-1
Expression of recombination antimicrobial protein PIL22-PBD-2 in Pichia pastoris and verification of its biological function in vitro
Abstract
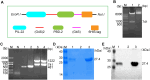
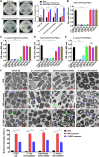
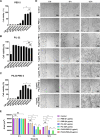
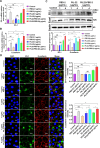
Finding suitable alternatives to antibiotics as feed additives is challenging for the livestock industry. Porcine beta-defensin 2 (PBD-2) is an endogenous antimicrobial peptide produced by pigs. Due to its broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against various microorganisms and its low tendency for drug resistance, it is considered a potential substitute for antibiotics. Additionally, given its strong ability to repair intestinal epithelial damage and maintain intestinal mucosal barrier function, porcine interleukin-22 (PIL-22) is a potential feed additive to combat intestinal damage caused by intestinal pathogens in piglets. In this study, the amino acid sequences of PBD-2 and PIL-22 were combined to express the fusion protein in Pichia pastoris, and its biological activity was evaluated in vitro. Our results showed that the PIL22-PBD-2 exhibits broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O8 (ETEC O8), Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella typhimurium, and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). PIL22-PBD-2 demonstrated wound repair capability through a healing assay in the intestinal porcine epithelial cell line-J2 (IPEC-J2). Furthermore, PIL22-PBD-2 significantly enhanced the expression of the major intercellular junction-associated proteins ZO-1 and E-cadherin in IPEC-J2. It is important to note that PIL22-PBD-2 reduced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis (p < 0.05) considerably and decreased bacterial adhesion (p < 0.05) in ETEC O8-challenged IPEC-J2. We also found that the PIL22-PBD-2 treatment attenuated ETEC O8-induced inflammatory responses in IPEC-J2 by exerting antibacterial activity, increasing the expression of endogenous antimicrobial peptides, and significantly decreasing the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α (p < 0.05). In conclusion, our studies demonstrate that PIL22-PBD-2 has a positive effect on inhibiting pathogenic bacteria and repairing intestinal damage.
Keywords: Antibiotic-resistant; eukaryotic expression; feed additive; intestinal repair; recombinant antimicrobial protein.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
L-Threonine upregulates the expression of β-defensins by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway and suppressing SIRT1 expression in porcine intestinal epithelial cells.Food Funct. 2021 Jul 5;12(13):5821-5836. doi: 10.1039/d1fo00269d. Food Funct. 2021. PMID: 34047325
-
β-defensin 118 attenuates inflammation and injury of intestinal epithelial cells upon enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Apr 19;18(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03242-3. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35440001 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of porcine beta-defensin 1 gene in Pichia pastoris].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006 Nov;22(6):1036-9. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 17168333 Chinese.
-
Porcine β-defensin-2 alleviates aflatoxin B1 induced intestinal mucosal damage via ROS-Erk1/2 signaling pathway.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Dec 20;905:167201. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167201. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37734607
-
Lactobacillus reuteri 1 Enhances Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function and Alleviates the Inflammatory Response Induced by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 via Suppressing the MLCK Signaling Pathway in IPEC-J2 Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 14;13:897395. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.897395. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murugaiyan J, Kumar PA, Rao GS, Iskandar K, Hawser S, Hays JP, Mohsen Y, Adukkadukkam S, Awuah WA, Jose RAM, Sylvia N, Nansubuga EP, Tilocca B, Roncada P, Roson-Calero N, Moreno-Morales J, Amin R, Kumar BK, Kumar A, Toufik AR, Zaw TN, Akinwotu OO, Satyaseela MP, van Dongen MBM (2022) Progress in alternative strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance: focus on antibiotics. Antibiotics 11:200 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu WT, Chen EZ, Yang L, Peng C, Wang Q, Xu Z, Chen DQ (2021) Emerging resistance mechanisms for 4 types of common anti-MRSA antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus: a comprehensive review. Microb Pathog 156:104915 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

