Evaluating the efficacy and safety of combined microneedling therapy versus topical Minoxidil in androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40056230
- PMCID: PMC11890238
- DOI: 10.1007/s00403-025-04032-1
Evaluating the efficacy and safety of combined microneedling therapy versus topical Minoxidil in androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
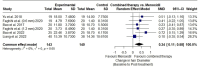
This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of the combined microneedling (CMNT) with minoxidil versus minoxidil monotherapy for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia (AGA), with a focus on the impact of microneedling parameters on treatment outcomes. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis (PROSPERO: CRD42024594487) of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing CMNT versus minoxidil alone for AGA, following PRISMA guidelines. A comprehensive search across six databases was performed up to September 8, 2024. We identified 12 RCTs involving 631 AGA patients, with a total of 11 RCTs included in the meta-analyses. CMNT significantly improved hair count compared to minoxidil monotherapy (SMD 1.32, 95% CI 0.73-1.92, p < 0.01), with substantial heterogeneity (I² = 88%, p < 0.01). Subgroup analyses indicated no significant effect of microneedling (MN) depth (≤ 1 mm vs. >1 mm), duration (≤ 12 weeks vs. >12 weeks), or technique(device) (electrodynamic vs. rolling) on hair count outcomes. Additionally, A meta-analysis of six RCTs demonstrated a significant improvement in hair diameter with CMNT (SMD 0.34, 95% CI 0.11-0.58; p < 0.01), with no observed heterogeneity (I² = 0%). Investigators and patient's self-assessment scores were also improved. Adverse events were more frequent with CMNT (74 vs. 59 events), however they were generally considered mild or self-limiting. CMNT significantly enhances hair count and diameter in AGA patients with mild adverse events. MN parameters including depth, duration, and technique variations did not significantly affect hair count outcome, suggesting microneedling as a promising adjunctive AGA treatment.
Keywords: Androgenetic alopecia; Depth; Diameter; Electrodynamic microneedling; Hair count; Hair diameter; Microneedling; Rolling microneedling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, Reygagne P, Finner A, Blumeyer A, Trakatelli M, Tosti A, del Marmol V, Piraccini BM (2018) Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men–short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 32:11–22 - PubMed
-
- Nussbaum D, Murphy E, Nelson K, Gonzalez-Lopez A, Qureshi A, Schwartz J, Friedman A (2022) A survey of patient attitudes towards topical Minoxidil in the treatment of hair loss. J Drugs Dermatol 21:1140–1142 - PubMed
-
- Inui S, Fukuzato Y, Nakajima T, Yoshikawa K, Itami S (2002) Androgen-inducible TGF‐β1 from balding dermal papilla cells inhibits epithelial cell growth: a clue to Understanding Paradoxical effects of androgen on human hair growth. FASEB J 16:1967–1969 - PubMed
-
- Inui S, Fukuzato Y, Nakajima T, Yoshikawa K, Itami S (2003) Identification of androgen-inducible TGF-β1 derived from dermal papilla cells as a key mediator in androgenetic alopecia. In: Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings. Elsevier, pp 69–71 - PubMed
-
- Lolli F, Pallotti F, Rossi A, Fortuna MC, Caro G, Lenzi A, Sansone A, Lombardo F (2017) Androgenetic alopecia: a review. Endocrine 57:9–17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

