From theory to therapy: unlocking the potential of muscarinic receptor activation in schizophrenia with the dual M1/M4 muscarinic receptor agonist xanomeline and trospium chloride and insights from clinical trials
- PMID: 40056428
- PMCID: PMC11997306
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaf015
From theory to therapy: unlocking the potential of muscarinic receptor activation in schizophrenia with the dual M1/M4 muscarinic receptor agonist xanomeline and trospium chloride and insights from clinical trials
Erratum in
-
Correction to: From theory to therapy: unlocking the potential of muscarinic receptor activation in schizophrenia with the dual M1/M4 muscarinic receptor agonist xanomeline and trospium chloride and insights from clinical trials.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2025 Jul 23;28(7):pyaf051. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaf051. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40698986 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
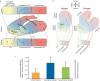
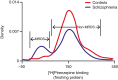
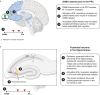
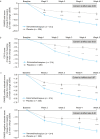
Since the 1950s, understanding of antipsychotic activity in schizophrenia has been largely grounded in the dopamine (DA) hypothesis. Most antipsychotics approved for schizophrenia interact with D2 DA receptors as an important part of their mechanism of action. While antipsychotics blocking D2 DA receptors can be effective for positive symptoms of schizophrenia, none are approved by regulatory authorities for predominant negative or cognitive symptoms. Moreover, many of these agents induce a range of problematic side effects related to D2 DA receptor blockade (eg, drug-induced parkinsonism, akathisia, tardive dyskinesia, hyperprolactinemia and related sexual side effects, sedation). This has prompted the search for novel mechanisms with improved efficacy and tolerability based on evidence supporting involvement of other neurotransmitter systems in schizophrenia pathophysiology, including acetylcholine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and glutamate. Among these options, targeting muscarinic receptors emerged as a promising treatment strategy. In September 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved xanomeline and trospium chloride for treatment of adults with schizophrenia based on results from three 5-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials and two 52-week open-label trials. In the placebo-controlled trials, xanomeline/trospium reduced symptoms of schizophrenia, was generally well tolerated, and was not associated with clinically meaningful motor symptoms, hyperprolactinemia, sexual side effects, or weight gain compared with placebo. The long-term safety of xanomeline/trospium was also confirmed in two 52-week, open-label trials. This paper reviews the preclinical and clinical rationale for muscarinic receptor activation as a treatment for schizophrenia and the efficacy, safety, and tolerability profile of xanomeline/trospium.
Keywords: KarXT; muscarinic receptors; psychosis; schizophrenia; xanomeline and trospium chloride.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Conflict of interest statement
In the prior 24 months, J.M.M. has received advising, consulting, and/or speaker fees from AbbVie, Alkermes, Axsome, BioXcel, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cerevel, Delpor, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Neurocrine, Noven, Otsuka America, Relmada, Sumitomo, and Teva. K.K., S.V., and I.K. are employees of Bristol Myers Squibb. A.C.M. is a consultant to Bristol Myers Squibb.
Figures


References
-
- Marder SR, Cannon TD. Schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:1753–1761. https://doi.org/ 10.1056/NEJMra1808803 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jauhar S, Johnstone M, McKenna PJ. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2022; 399:473–486. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01730-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weye N, Santomauro DF, Agerbo E, et al. Register-based metrics of years lived with disability associated with mental and substance use disorders: a register-based cohort study in Denmark. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021; 8:310–319. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00029-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017; 390:1211–1259. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olfson M, Gerhard T, Huang C, Crystal S, Stroup TS. Premature mortality among adults with schizophrenia in the United States. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015; 72:1172–1181. https://doi.org/ 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.1737 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

