Haploinsufficiency of ITSN1 is associated with a substantial increased risk of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40056900
- PMCID: PMC12124131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115355
Haploinsufficiency of ITSN1 is associated with a substantial increased risk of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Despite its significant heritability, the genetic basis of Parkinson's disease (PD) remains incompletely understood. Here, in analyzing whole-genome sequence data from 3,809 PD cases and 247,101 controls in the UK Biobank, we discover that protein-truncating variants in ITSN1 confer a substantially increased risk of PD (p = 6.1 × 10-7; odds ratio [95% confidence interval] = 10.5 [5.2, 21.3]). We replicate this association in three independent datasets totaling 8,407 cases and 413,432 controls (combined p = 4.5 × 10-12). Notably, ITSN1 haploinsufficiency has also been associated with autism spectrum disorder, suggesting variable penetrance/expressivity. In Drosophila, we find that loss of the ITSN1 ortholog Dap160 exacerbates α-synuclein-induced neuronal toxicity and motor deficits, and in vitro assays further suggest a physical interaction between ITSN1 and α-synuclein. These results firmly establish ITSN1 as a PD risk gene with an effect size exceeding previously established loci, implicate vesicular trafficking dysfunction in PD pathogenesis, and potentially open new avenues for therapeutic development.
Keywords: CP: Genomics; ITSN1; Intersectin 1; Parkinson's disease; SNCA; autism; endocytosis; neurodegeneration; rare variants; synaptic transmission; synuclein.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.P.S., J.M., F.H., Q.W., D.V., M.G., L.M., M.M., G.D.A., B.H., S.P., and I.T. are current employees and/or shareholders of AstraZeneca. R.S.D. is a paid consultant of AstraZeneca. H.Y.Z. is a member of the Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Board of Directors, co-founder of Cajal Neuroscience, and on the science advisory board of the Column group. J.M.S. received research support from Regeneron Genetics Center.
Figures
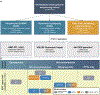

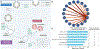


References
-
- Nalls MA, Blauwendraat C, Vallerga CL, Heilbron K, Bandres-Ciga S, Chang D, Tan M, Kia DA, Noyce AJ, Xue A, et al. (2019). Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-genome wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 18, 1091–1102. 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30320-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

