LTA4H improves the tumor microenvironment and prevents HCC progression via targeting the HNRNPA1/LTBP1/TGF-β axis
- PMID: 40056904
- PMCID: PMC11970384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102000
LTA4H improves the tumor microenvironment and prevents HCC progression via targeting the HNRNPA1/LTBP1/TGF-β axis
Abstract
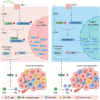
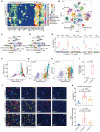
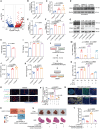
Leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H), an inflammatory mediator, has garnered attention for its role in the development of chronic lung diseases and various cancers. Our study highlights the protective role of LTA4H in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) occurrence and progression. LTA4H is downregulated in clinical and mouse HCC tumors. LTA4H deficiency exacerbates hepatocyte damage by restraining JNK activation and promotes CD206+ macrophage polarization through the upregulation of LTBP1 expression and downstream transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) secretion and activation. Mechanistically, LTA4H induces heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (HNRNPA1) phosphorylation, enhancing their interaction and leading to the functional inhibition of HNRNPA1 in regulating Ltbp1 mRNA maturation and processing in the nucleus. LTA4H-deficient patients exhibit poor prognosis and immunotherapy resistance. Combination therapy targeting TGF-β and PD-1 significantly improves the immunotherapy resistance of LTA4H-knockout Hepa1-6 tumors. Our findings reveal the previously unreported role of LTA4H in regulating the tumor microenvironment and provide insights into potential diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for patients with LTA4H-deficient HCC.
Keywords: BLT1; CD206(+) macrophage; H3K27ac; HDAC1; HNRNPA1; LTA4H; LTBP1; TGF-β; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy resistance.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.W., S.Y., and L.C. are inventors on a provisional China patent application related to this work (serial no. 202410654363.0, filed on 24 May 2024).
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

