Nano-chitosan hydrogel alleviates Candida albicans-induced health alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): antioxidant response, neuro-behaviors, hepato-renal functions, and histopathological investigation
- PMID: 40057767
- PMCID: PMC11889809
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-025-04568-4
Nano-chitosan hydrogel alleviates Candida albicans-induced health alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): antioxidant response, neuro-behaviors, hepato-renal functions, and histopathological investigation
Abstract
Background: Candida albicans infection induces economic losses in aquaculture practices. Currently, the success of the nanotechnology field has gained more consideration in the aquaculture sector as it bestows favorable impacts in remedies in comparison to traditional practices.
Objective: The present study was conducted to assess the role of nano chitosan gel (NCG) exposure via water in managing the deteriorating impacts triggered by C. albicans in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Hepato-renal function, behavioral and stress response, neurological function, hepatic antioxidant/oxidant status, and histopathological architectures were investigated.
Methods: A total of 160 fish (average weight: 50.00 ± 6.30 g) were randomly assigned to four groups, each with four replicates: control, NCG, C. albicans, and NCG + C. albicans. The NCG was applied as bath treatment at a concentration of 75 µg/L for ten days.
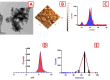
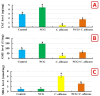
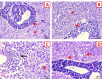
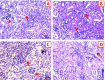
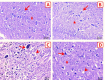
Results: The outcomes demonstrated that the C. albicans challenged fish exhibited obvious behavioral alterations including loss of equilibrium, surfacing, abnormal swimming and movement, and aggression. Infection with C. albicans caused an elevation in hepato-renal biomarkers (alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, alkaline phosphatase, urea, and creatinine), stress-related indices (glucose, cortisol, nor-epinephrine, and 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine), and lipid peroxides (malondialdehyde). Moreover, it caused a noticeable decline in the hepatic antioxidant indices (total antioxidant capacity and reduced glutathione content) and acetylcholinesterase activity. The hepatic, renal, and brain architectures were severely damaged by the C. albicans challenge, exhibiting significant fatty changes, necrosis, vacuolation, and congestion. Remarkably, the aqueous application of NCG in the C. albicans-challenged fish ameliorated all the aforementioned biomarkers and facilitated the regeneration of histopathological changes.
Conclusion: Overall, the application of NCG in the aquatic environment is an effective tool for managing C. albicans infection in Nile tilapia. Moreover, it can be utilized in combating stress conditions in the aquaculture sector.
Keywords: Candida albicans; Antioxidant status; Biological stress; Histopathology; Nano chitosan gel; Nile tilapia.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Zagazig University, Egypt approved the experimental protocol (ZUIACUC–2-F–333–2022). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Informed consent has been obtained from the private farm owners. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ibrahim RE, Elshopakey GE, Abd El-Rahman GI, Ahmed AI, Altohamy DE, Zaglool AW, Younis EM, Abdelwarith AA, Davies SJ, Al-Harthi HF, et al. Palliative role of colloidal silver nanoparticles synthetized by moringa against Saprolegnia spp. infection in Nile Tilapia: Biochemical, immuno-antioxidant response, gene expression, and histopathological investigation. Aquac Rep. 2022;26:101318. - DOI
-
- Tartor Y, Taha M, Mahboub H, El Ghamery M. Yeast species associated with diseased fish: occurrence, identification, experimental challenges and antifungal susceptibility testing. Aquaculture. 2018;488:134–44. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

