Analysis of Limited Proteolysis-Coupled Mass Spectrometry Data
- PMID: 40058498
- PMCID: PMC12036054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.100934
Analysis of Limited Proteolysis-Coupled Mass Spectrometry Data
Abstract
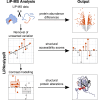
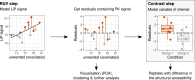
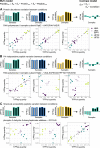
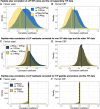
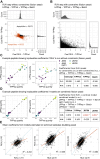
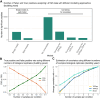
Limited proteolysis combined with mass spectrometry (LiP-MS) facilitates probing structural changes on a proteome-wide scale. This method leverages differences in the proteinase K accessibility of native protein structures to concurrently assess structural alterations for thousands of proteins in situ. Distinguishing different contributions to the LiP-MS signal, such as changes in protein abundance or chemical modifications, from structural protein alterations remains challenging. Here, we present the first comprehensive computational pipeline to infer structural alterations for LiP-MS data using a two-step approach. 1) We remove unwanted variations from the LiP signal that are not caused by protein structural effects and 2) infer the effects of variables of interest on the remaining signal. Using LiP-MS data from three species, we demonstrate that this approach outperforms previously employed approaches. Our framework provides a uniquely powerful approach for deconvolving LiP-MS signals and separating protein structural changes from changes in protein abundance, posttranslational modifications, and alternative splicing. Our approach may also be applied to analyze other types of peptide-centric structural proteomics data, such as FPOP or molecular painting data.
Keywords: MS data analysis; R package; limited proteolysis-coupled mass spectrometry (LiP-MS); protein structure; proteomics data analysis; statistical modelling.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest P. P. is a scientific advisor for the company Biognosys AG (Zurich, Switzerland) and an inventor of a patent licensed by Biognosys AG that covers the LiP-MS method used in this protocol. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Henzler-Wildman K., Kern D. Dynamic personalities of proteins. Nature. 2007;450:964–972. - PubMed
-
- Tzeng S.-R., Kalodimos C.G. Protein activity regulation by conformational entropy. Nature. 2012;488:236–240. - PubMed
-
- Feng Y., De Franceschi G., Kahraman A., Soste M., Melnik A., Boersema P.J., et al. Global analysis of protein structural changes in complex proteomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014;32:1036–1044. - PubMed
-
- Savitski M.M., Reinhard F.B.M., Franken H., Werner T., Savitski M.F., Eberhard D., et al. Tracking cancer drugs in living cells by thermal profiling of the proteome. Science. 2014;346 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

