This is a preprint.
Resistance to Radiation Enhances Metastasis by Altering RNA Metabolism
- PMID: 40060410
- PMCID: PMC11888214
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.02.19.638943
Resistance to Radiation Enhances Metastasis by Altering RNA Metabolism
Abstract
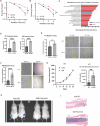
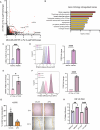
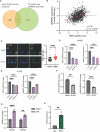
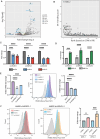
The cellular programs that mediate therapy resistance are often important drivers of metastasis, a phenomenon that needs to be understood better to improve screening and treatment options for cancer patients. Although this issue has been studied extensively for chemotherapy, less is known about a causal link between resistance to radiation therapy and metastasis. We investigated this problem in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and established that radiation resistant tumor cells have enhanced metastatic capacity, especially to bone. Resistance to radiation increases the expression of integrin β3 (ITGβ3), which promotes enhanced migration and invasion. Bioinformatic analysis and subsequent experimentation revealed an enrichment of RNA metabolism pathways that stabilize ITGβ3 transcripts. Specifically, the RNA binding protein heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L (HNRNPL), whose expression is regulated by Nrf2, mediates the formation of circular RNAs (circRNAs) that function as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) for the family of let-7 microRNAs that target ITGβ3. Collectively, our findings identify a novel mechanism of radiation-induced metastasis that is driven by alterations in RNA metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors have no conflicting interests
Figures

Similar articles
-
The metastasis suppressor NME1 inhibits melanoma cell motility via direct transcriptional induction of the integrin beta-3 gene.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Jan 1;374(1):85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30458180 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Alterations Affecting Competitive Endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and Regulatory Networks (ceRNETs) with Clinical Implications in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 23;25(5):2624. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052624. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA-associated ceRNA network involved in HIF-1 signalling in triple-negative breast cancer: circ_0047303 as a potential key regulator.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Dec;25(24):11322-11332. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17066. Epub 2021 Nov 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34791795 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Insights into Competitive Endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) Regulated Pathogenic Mechanisms in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (mTNBC).Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 1;16(17):3057. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173057. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circGFRA1 and GFRA1 act as ceRNAs in triple negative breast cancer by regulating miR-34a.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 16;36(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0614-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29037220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biomechanical regulation of breast cancer metastasis and progression | Scientific Reports [Internet]. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-89288-z. Accessed November 1, 2024. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
