This is a preprint.
Apolipoprotein E abundance is elevated in the brains of individuals with Down syndrome-Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40060680
- PMCID: PMC11888362
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.02.24.639862
Apolipoprotein E abundance is elevated in the brains of individuals with Down syndrome-Alzheimer's disease
Update in
-
Apolipoprotein E abundance is elevated in the brains of individuals with Down syndrome-Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2025 May 19;149(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s00401-025-02889-0. Acta Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 40387921 Free PMC article.
Abstract
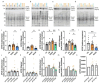
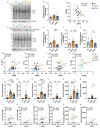
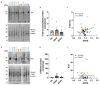
Trisomy of chromosome 21, the cause of Down syndrome (DS), is the most commonly occurring genetic cause of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here, we compare the frontal cortex proteome of people with Down syndrome-Alzheimer's disease (DSAD) to demographically matched cases of early-onset AD and healthy ageing controls. We find wide dysregulation of the proteome, beyond proteins encoded by chromosome 21, including an increase in the abundance of the key AD-associated protein, APOE, in people with DSAD compared to matched cases of AD. To understand the cell types that may contribute to changes in protein abundance, we undertook a matched single-nuclei RNA-sequencing study, which demonstrated that APOE expression was elevated in subtypes of astrocytes, endothelial cells and pericytes in DSAD. We further investigate how trisomy 21 may cause increased APOE. Increased abundance of APOE may impact the development of, or response to, AD pathology in the brain of people with DSAD, altering disease mechanisms with clinical implications. Overall, these data highlight that trisomy 21 alters both the transcriptome and proteome of people with DS in the context of AD, and that these differences should be considered when selecting therapeutic strategies for this vulnerable group of individuals who have high-risk of early-onset dementia.
Keywords: Amyloid Precursor protein; ApoE; Trisomy 21; frontal cortex; mass spectrometry; neuropathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alić I, Goh PA, Murray A, Portelius E, Gkanatsiou E, Gough G, Mok KY, Koschut D, Brunmeir R, Yeap YJ, O’Brien NL, Groet J, Shao X, Havlicek S, Dunn NR, Kvartsberg H, Brinkmalm G, Hithersay R, Startin C, Hamburg S, Phillips M, Pervushin K, Turmaine M, Wallon D, Rovelet-Lecrux A, Soininen H, Volpi E, Martin JE, Foo JN, Becker DL, Rostagno A, Ghiso J, Krsnik Ž, Šimić G, Kostović I, Mitrečić D, Francis PT, Blennow K, Strydom A, Nizetic D, Hardy J, Zetterberg H, Nižetić D (2021) Patient-specific Alzheimer-like pathology in trisomy 21 cerebral organoids reveals BACE2 as a gene dose-sensitive AD suppressor in human brain. Mol Psychiatry 26:5766–5788. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0806-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bejanin A, Iulita MF, Vilaplana E, Carmona-Iragui M, Benejam B, Videla L, Barroeta I, Fernandez S, Altuna M, Pegueroles J, Montal V, Valldeneu S, Giménez S, González-Ortiz S, Muñoz L, Padilla C, Aranha MR, Estellés T, Illán-Gala I, Belbin O, Camacho V, Wilson LR, Annus T, Osorio RS, Videla S, Lehmann S, Holland AJ, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Alcolea D, Clarimon J, Zaman SH, Blesa R, Lleó A, Fortea J (2021) Association of Apolipoprotein E ε4 Allele With Clinical and Multimodal Biomarker Changes of Alzheimer Disease in Adults With Down Syndrome. JAMA Neurol 78:937–947. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.1893 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boerwinkle AH, Gordon BA, Wisch J, Flores S, Henson RL, Butt OH, McKay N, Chen CD, Benzinger TLS, Fagan AM, Handen BL, Christian BT, Head E, Mapstone M, Rafii MS, O’Bryant S, Lai F, Rosas HD, Lee JH, Silverman W, Brickman AM, Chhatwal JP, Cruchaga C, Perrin RJ, Xiong C, Hassenstab J, McDade E, Bateman RJ, Ances BM, Aizenstein HJ, Andrews HF, Bell K, Birn RM, Bulova P, Cheema A, Chen K, Clare I, Clark L, Cohen AD, Constantino JN, Doran EW, Feingold E, Foroud TM, Hartley SL, Hom C, Honig L, Ikonomovic MD, Johnson SC, Jordan C, Kamboh MI, Keator D, Klunk MD WE, Kofler JK, Kreisl WC, Krinsky- McHale SJ, Lao P, Laymon C, Lott IT, Lupson V, Mathis CA, Minhas DS, Nadkarni N, Pang D, Petersen M, Price JC, Pulsifer M, Reiman E, Rizvi B, Sabbagh MN, Schupf N, Tudorascu DL, Tumuluru R, Tycko B, Varadarajan B, White DA, Yassa MA, Zaman S, Zhang F, Adams S, Allegri R, Araki A, Barthelemy N, Bechara J, Berman S, Bodge C, Brandon S, Brooks W, Brosch J, Buck J, Buckles V, Carter K, Cash L, Mendez PC, Chua J, Chui H, Courtney L, Day G, DeLaCruz C, Denner D, Diffenbacher A, Dincer A, Donahue T, Douglas J, Duong D, Egido N, Esposito B, Farlow M, Feldman B, Fitzpatrick C, Fox N, Franklin E, Joseph-Mathurin N, Fujii H, Gardener S, Ghetti B, Goate A, Goldberg S, Goldman J, Gonzalez A, Gräber-Sultan S, Graff-Radford N, Graham M, Gray J, Gremminger E, Grilo M, Groves A, Haass C, Häslerc L, Hellm C, Herries E, Hoechst-Swisher L, Hofmann A, Holtzman D, Hornbeck R, Igor Y, Ihara R, Ikeuchi T, Ikonomovic S, Ishii K, Jack C, Jerome G, Johnson E, Jucker M, Karch C, Käser S, Kasuga K, Keefe S, Klunk W, Koeppe R, Koudelis D, Kuder-Buletta E, Laske C, Levey A, Levin J, Li Y, Lopez O, Marsh J, Martins R, Mason NS, Masters C, Mawuenyega K, McCullough A, Mejia A, Morenas-Rodriguez E, Morris JC, Mountz J, Mummery C, Nadkarni N, Nagamatsu A, Neimeyer K, Niimi Y, Noble J, Norton J, Nuscher B, Obermüller U, O’Connor A, Patira R, Ping L, Preische O, Renton A, Ringman J, Salloway S, Schofield P, Senda M, Seyfried NT, Shady K, Shimada H, Sigurdson W, Smith J, Smith L, Snitz B, Sohrabi H, Stephens S, Taddei K, Thompson S, Vöglein J, Wang P, Wang Q, Weamer E, Xu J, Xu X (2023) Comparison of amyloid burden in individuals with Down syndrome versus autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol 22:55–65. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00408-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
