Enhanced Cartilage Regeneration: Chemical, Mechanical, and In Vitro Analysis of Innovative TiO2-Reinforced PVA Implants
- PMID: 40060854
- PMCID: PMC11886706
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07029
Enhanced Cartilage Regeneration: Chemical, Mechanical, and In Vitro Analysis of Innovative TiO2-Reinforced PVA Implants
Abstract
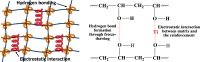
This study focuses on developing a synthetic, biocompatible graft for treating cartilage lesions. One-dimensional titanium dioxide nanotubes (TNTs) were incorporated into poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) hydrogel and processed using freeze-drying without chemical surfactants. Upon optimization of the composition, it was found that the incorporation of TNT altered the biomechanical properties without causing any adverse physiological effects. Annealing treatment further enhanced mechanical strength and energy dissipation, promoting elasticity. The hydrogel with 2 wt % TNT achieved maximum mechanical strength and the storage modulus values indicated elastic dominance, and biotribological tests showed cartilage-like frictional response via hydrodynamic lubrication. Against the microorganisms Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans, grafts showed significant antimicrobial activity. In vitro experiments demonstrated that these nanocomposite hydrogels supported adhesion, proliferation, and upregulation of cartilage-specific gene expression in human mesenchymal stem cells hMSCs. This suggests potential for promoting hMSC chondrogenic differentiation and accelerating cartilage regeneration.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures















References
-
- Yao H.; Kang J.; Li W.; Liu J.; Xie R.; Wang Y.; Liu S. Novel β-TCP/PVA bilayered hydrogels with considerable physical and bio-functional properties for osteochondral repair Novel β -TCP/PVA bilayered hydrogels with considerable physical and bio-functional properties for osteochondral repair. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 13, 01501210.1088/1748-605X/aa8541. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
