Exploring the relationship between physical activity and smartphone addiction among college students in Western China
- PMID: 40061470
- PMCID: PMC11885492
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1530947
Exploring the relationship between physical activity and smartphone addiction among college students in Western China
Abstract
Background: Smartphone addiction (SA) refers to a behavioral disorder characterized by an irresistible compulsion to excessively engage with mobile devices. Currently, the evidence regarding the relationship between physical activity (PA), exercise intensity (EI), and SA is limited, particularly within Chinese populations. This study aims to explore the correlation between PA, EI, and SA, specifically investigating how PA and EI impact SA to better understand the nature of this relationship.
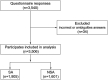
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted involving college students from over 20 universities in Western China. Data were collected on participants' engagement in PA, EI, and SA. Additionally, covariates such as age, gender, ethnicity, academic classification, university location, discipline, year of study, hometown region, sibling status, relationship status, and social interactions were recorded. Multivariate logistic regression models were used to assess the association between PA, EI, and SA. Stratified and interaction analyses were performed to examine whether the relationship remained consistent across different subgroups.
Results: Of the 3,506 college students surveyed, 1,905 (54.3%) experienced SA. The prevalence of SA was 11.3% lower in the group that engaged in PA compared to those who did not. In the fully adjusted model, PA was negatively associated with SA (OR = 0.70, 95% CI: 0.59-0.82, p < 0.001). EI was also inversely associated with SA. Moderate- and vigorous-intensity exercise had odds ratios of 0.81 (95% CI: 0.67-0.98, p = 0.034) and 0.83 (95% CI: 0.68-1.00, p = 0.046), respectively, compared with low-intensity exercise. Similar patterns were observed in subgroup analyses (all p values for interaction >0.05).
Conclusion: The findings indicate a significant negative association between PA, EI, and SA, highlighting the potential of promoting PA and higher EI as strategies to reduce SA among college students.
Keywords: Western China; college students; cross-sectional survey; exercise intensity; physical activity; smartphone addiction.
Copyright © 2025 Lai, Cai, Liao, Li, Wang, Wang, Ye, Chen, Hambly, Yu, Bao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Government P . China officially begins commercial use of 5G. (2019). Available from: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-06/07/content_5398188.htm (Accessed on 2024-08-01)
-
- CNNIC . (2024). The 53rd Statistical Report of China's Internet Development. Available from: https://www.cnnic.net.cn/n4/2024/0321/c208-10962.html (Accessed on 2024-08-01)
-
- CNNIC . The 47rd Statistical Report of China's Internet Development. (2021). Available from: https://www.cnnic.cn/n4/2022/0401/c88-1125.html (Accessed on 2024-08-01)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

