Antiviral potential of ginseng: Targeting human pathogenic viruses with compounds derived from ginseng
- PMID: 40061485
- PMCID: PMC11889387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.12.004
Antiviral potential of ginseng: Targeting human pathogenic viruses with compounds derived from ginseng
Abstract
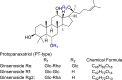
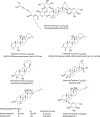
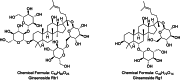
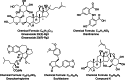
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the critical need for effective antiviral therapies, as viral infections remain a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Natural compounds, especially those derived from plants, have been recognized for their therapeutic properties. Ginseng, in particular, has attracted considerable attention for its potential antiviral effects. This review examines the antiviral compounds from ginseng that act against various human pathogenic viruses. We systematically summarize the antiviral activities of ginseng compounds targeting a range of viruses, including human rhinovirus (HRV), influenza virus, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis viruses A, B, and C (HAV, HBV, HCV), herpes simplex virus (HSV), enterovirus 71 (EV71), coxsackievirus, norovirus, and SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. This review covers Panax ginseng, P. notoginseng, and P. quinquefolius, discussing their mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential. The analysis incorporates literature from February 2002 through August 2024, providing a comprehensive overview of the existing evidence on the antiviral properties of compounds derived from ginseng. This review aims to underscore the scientific basis for developing ginseng as an antiviral therapeutic agent or nutraceutical.
Keywords: Antiviral effect; Ginseng; Ginseng-derived compounds; Human pathogenic viruses.
© 2025 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antiviral Potential of the Genus Panax: An updated review on their effects and underlying mechanism of action.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Mar;47(2):183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.11.003. Epub 2022 Nov 17. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 36926608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginseng, the natural effectual antiviral: Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against viral infection.J Ginseng Res. 2016 Oct;40(4):309-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Ginseng Res. 2016. PMID: 27746682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Antiviral activity of extracts of basidiomycetes and humic compounds substances against Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Retroviridae: Orthoretrovirinae: Lentivirus: Human immunodeficiency virus 1) and Herpes Simplex Virus (Herpesviridae: Simplexvirus: Human alphaherpesvirus 1)].Vopr Virusol. 2020 Nov 14;65(5):276-283. doi: 10.36233/0507-4088-2020-65-5-4. Vopr Virusol. 2020. PMID: 33533211 Russian.
-
Antiviral potential of garlic (Allium sativum) and its organosulfur compounds: A systematic update of pre-clinical and clinical data.Trends Food Sci Technol. 2020 Oct;104:219-234. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.08.006. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32836826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Bioactive Compounds: Their Activities and Underlying Mechanisms Against Human Viral Infections.Recent Adv Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2025 Apr 22. doi: 10.2174/0127724344376918250328054623. Online ahead of print. Recent Adv Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 40265436
References
-
- Forterre P., Prangishvili D. The great billion‐year war between ribosome‐and capsid‐encoding organisms (cells and viruses) as the major source of evolutionary novelties. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1178(1):65–77. - PubMed
-
- Dinesh D.C., Tamilarasan S., Rajaram K., Bouřa E. Antiviral drug targets of single-stranded RNA viruses causing chronic human diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(2):105–124. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

