DNA methylation signatures of cervical pre-invasive and invasive disease: An epigenome-wide association study
- PMID: 40065506
- PMCID: PMC12079623
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.35406
DNA methylation signatures of cervical pre-invasive and invasive disease: An epigenome-wide association study
Abstract
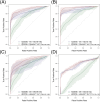
Epigenetic alterations are essential in the development of cancers, while epigenome-wide exploration in cervical cancer has been limited. In this epigenome-wide association study (EWAS) we explore differential DNA methylation signatures associated with CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia) grade 3 and cervical cancer to better understand potential drivers and biomarkers of cervical carcinogenesis. 247 women were recruited between 2014 and 2020 (N = 119 benign, N = 74 CIN3/CGIN [cervical glandular intraepithelial neoplasia] and N = 54 cancer). Methylation signatures were obtained from exfoliated cervical cells and sequenced using the Illumina 850 k array. Logistic regression and conditional analyses were used to test for independent associations between Cytosine-phosphate-Guanine (CpG) sites and case-control status, with adjustment for batch, chip, age, and human papillomavirus (HPV) status. 409 CpG sites were strongly associated with CIN3/cancer (p-value <5 × 10-8). Following conditional analysis, two CpG sites located in PAX1 (cg16767801) and NREP-AS1 genes (cg23642047) were independently associated with case status, yielding an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.92 (AUC = 0.97 for invasive disease). In a validation dataset (CIN3 only) PAX1/NREP-AS1 yielded a combined AUC of 0.77. Methylation markers offer promise for use in cervical screening, particularly as triage tests and self-sampling. We have identified a novel combined methylation marker that offers a high accuracy for the detection of CIN3 or worse.
Keywords: EWAS; PAX; cervical cancer; cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; epigenome; human papillomavirus; methylation.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
MC‐H holds shares in the O‐SMOSE company. Consulting activities conducted by the company are independent of the present study. All other authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures