Neutralizing Activity and T-Cell Responses Against Wild Type SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Omicron BA.5 Variant After Ancestral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Booster Dose in PLWH Receiving ART Based on CD4 T-Cell Count
- PMID: 40065712
- PMCID: PMC11893351
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e28
Neutralizing Activity and T-Cell Responses Against Wild Type SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Omicron BA.5 Variant After Ancestral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Booster Dose in PLWH Receiving ART Based on CD4 T-Cell Count
Abstract
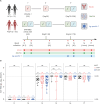
Background: We evaluated severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)-specific humoral and cellular responses for up to 6 months after the 3rd dose of ancestral coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in people living with HIV (PLWH) and healthy controls (HCs) who were not infected with COVID-19.
Methods: Anti-spike receptor-binding domain IgG (anti-RBD IgG) concentrations using chemiluminescence immunoassay and neutralizing antibodies using focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT) were assessed at 1 week after each dose of vaccination, and 3 and 6 months after the 3rd dose in 62 PLWH and 25 HCs. T-cell responses using intracellular cytokine stain were evaluated at 1 week before, and 1 week and 6 months after the 3rd dose.
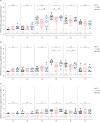
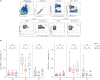
Results: At 1 week after the 3rd dose, adequate anti-RBD IgG (> 300 binding antibody unit /mL) was elicited in all PLWH except for one patient with 36 CD4 T-cell count/mm³. The geometric mean titers of 50% FRNT against wild type (WT) and omicron BA.5 strains of SARS-CoV-2 in PLWH with CD4 T-cell count ≥ 500 cells/mm³ (high CD4 recovery, HCDR) were comparable to HC, but they were significantly decreased in PLWH with CD4 T-cell count < 500/mm³ (low CD4 recovery, LCDR). After adjusting for age, gender, viral suppression, and number of preexisting comorbidities, CD4 T-cell counts < 500/mm³ significantly predicted a poor magnitude of neutralizing antibodies against WT, omicron BA.5, and XBB 1.5 strains among PLWH. Multivariable linear regression adjusting for age and gender revealed that LCDR was associated with reduced neutralizing activity (P = 0.017) and interferon-γ-producing T-cell responses (P = 0.049 for CD T-cell; P = 0.014 for CD8 T-cell) against WT, and strongly associated with more decreased cross-neutralization against omicron BA.5 strains (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: HCDR demonstrated robust humoral and cell-mediated immune responses after a booster dose of ancestral SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, whereas LCDR showed diminished immune responses against WT virus and more impaired cross-neutralization against omicron BA.5 strain.
Keywords: COVID-19 Vaccines; Cellular Immunity; HIV; Neutralizing Antibodies.
© 2025 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection affects adaptive immune responses to Omicron BA.4/BA.5 mRNA booster.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Jun;155(6):2038-2051. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.02.026. Epub 2025 Mar 3. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40044048
-
Neutralizing antibody responses and cellular responses against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants after mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in kidney transplant recipients.Sci Rep. 2024 May 28;14(1):12176. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63147-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38806644 Free PMC article.
-
Diversified humoral immunity and impacts of booster vaccines: SARS-CoV-2 antibody profile and Omicron BA.2 neutralization before and after first or second boosters.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0060524. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00605-24. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39162540 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking Optimal Immunogens to Face SARS-CoV-2 Evolution Through Vaccination.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2025 Jan;19(1):e70076. doi: 10.1111/irv.70076. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2025. PMID: 39871737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Durability of immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination.Semin Immunol. 2024 May;73:101884. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2024.101884. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Semin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38861769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

