Pulmonary Hypertension: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Studies
- PMID: 40066229
- PMCID: PMC11892029
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70134
Pulmonary Hypertension: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Studies
Abstract
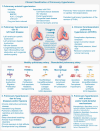
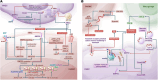
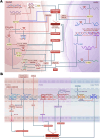
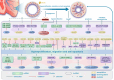
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) stands as a tumor paradigm cardiovascular disease marked by hyperproliferation of cells and vascular remodeling, culminating in heart failure. Complex genetic and epigenetic mechanisms collectively contribute to the disruption of pulmonary vascular homeostasis. In recent years, advancements in research technology have identified numerous gene deletions and mutations, in addition to bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2, that are closely associated with the vascular remodeling process in PH. Additionally, epigenetic modifications such as RNA methylation, DNA methylation, histone modification, and noncoding RNAs have been shown to precisely regulate PH molecular networks in a cell-type-specific manner, emerging as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. This review summarizes and analyzes the roles and molecular mechanisms of currently identified genes and epigenetic factors in PH, emphasizing the pivotal role of long ncRNAs in its regulation. Additionally, it examines current clinical and preclinical therapies for PH targeting these genes and epigenetic factors and explores potential new treatment strategies.
Keywords: clinical therapeutics; epigenetic; genetic; noncoding RNAs; pulmonary hypertension.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Virani S. S., Alonso A., Aparicio H. J., et al., “Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics‐2021 Update: a Report from the American Heart Association,” Circulation 143, no. 8 (2021): e254–e743. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
