A Rare Case of PRKACA Duplication-Associated Childhood-Onset Primary Pigmented Nodular Adrenocortical Disease
- PMID: 40066253
- PMCID: PMC11891440
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luaf035
A Rare Case of PRKACA Duplication-Associated Childhood-Onset Primary Pigmented Nodular Adrenocortical Disease
Abstract
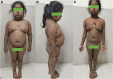
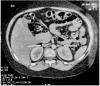
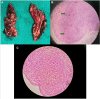
Primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease (PPNAD) is a rare but important cause of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-independent Cushing syndrome (CS). It usually presents as cyclical CS in young adults. Childhood onset of PPNAD is exceedingly rare. About 90% of cases of PPNAD are associated with Carney complex (CNC). Both PPNAD and CNC are linked to diverse pathogenic variants of the PRKAR1A gene, which encodes the regulatory subunit type 1 alpha of protein kinase A (PKA). Pathogenic variants of PRKACA gene, which encodes the catalytic subunit alpha of PKA, are extremely rare in PPNAD. We report a case of a female child, aged 8 years and 3 months, who presented with features suggestive of CS, including obesity, short stature, hypertension, moon facies, acne, and facial plethora but without classical striae or signs of CNC. Hormonal evaluation confirmed ACTH-independent CS. However, abdominal imaging revealed normal adrenal morphology. Genetic analysis identified a duplication of the PRKACA gene on chromosome 19p, which is linked to PPNAD. The patient underwent bilateral laparoscopic adrenalectomy, and histopathological study confirmed the PPNAD diagnosis. Postoperative follow-up showed resolution of cushingoid features and hypertension. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a female child with PRKACA duplication presenting as CS due to PPNAD.
Keywords: Carney complex; Cushing syndrome; PPNAD; PRKACA.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Auchus RJ, Flück CE, Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Elsevier; 2018:494‐495.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
